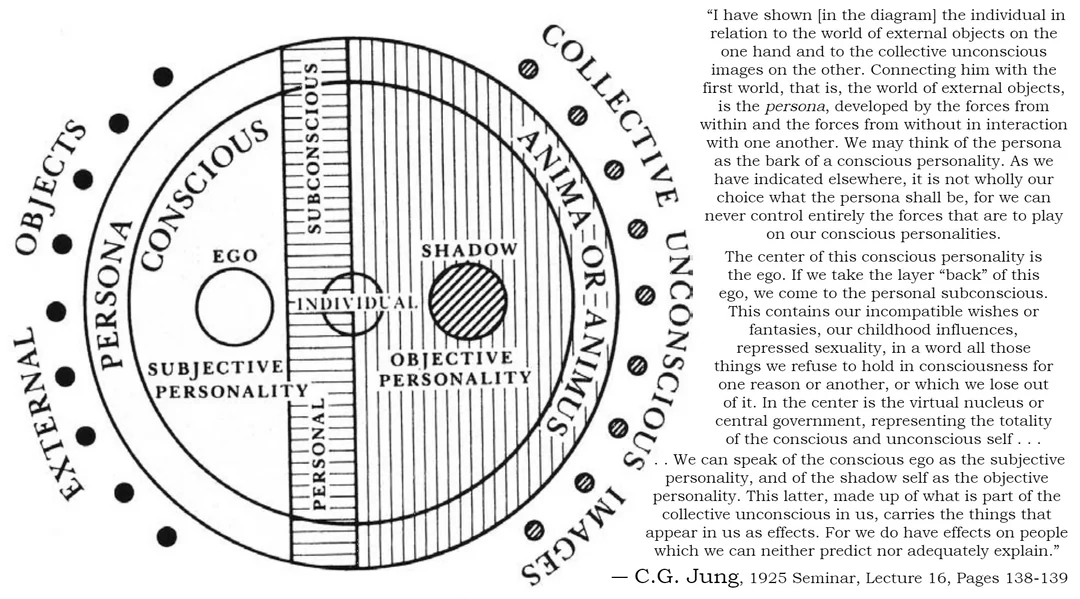
Navigating Uncertainty, and Finding Meaning in a Fractured World
Our era is characterized by the dominance of hyper-rationality and the relentless pursuit of objective truth, production, accomplishment and consumption. The human psyche finds itself adrift in a sea of fragmented images and disconnected meanings as the previous myths that used to give us purpose are exposed as hollow or erroneous. I see patients everyday that describe this phenomenon but not in these words. It is as if they are saying that they do not know who they are anymore. Not because they have changed but because all of the nodes and references points that used to contextualize their identity are stripped away or have been made foreign and incomprehensible. However the world still looks the same to them, despite its alienating effect. It is not the aesthetics of the world that are different, but the effect that it has on us. Because the world looks the same we feel crazy. Really it is our feelings telling us that the world is crazy even though it looks the same.
Effective therapy in the modern world needs to get over its insecurities of feeling or looking crazy. If we don’t let ourselves as therapists admit to patients that we also feel in pain, that we also feel crazy from these same forces, then how can therapy do anything but gaslight our patients more. When I see the news I feel like I am on drugs, even though I am stone cold sober. I know that the people on tv do not believe the things they say and are not acting for the reasons that they tell me as a spectator that they are. I am not a politician or a god, I am a therapist. I am as paralyzed against these forces as my patients are and yet I must help them recon with them. I must help them reckon with them even though I do not know how to reckon with them myself.
I didn’t understand it at first but have come around to the line of W.H. Auden that the Jungian analyst James Hillman liked to quote at the end of his life.
“We are lived by forces that we pretend to understand.”
-W. H. Auden
Auden’s line highlights how the frameworks and philosophies we resort to for certainty and order are often little more than self-delusion. The grand meaning-making systems of religion, science, politics, etc. that have risen to such cultural dominance are but feeble attempts to exert control over the ineffable complexities of being.
Yet we cling tenaciously to these conceptual constructs, these hyper-real simulations, because the alternative – admitting the primacy of ambiguity, contradiction, and the unfathomable depths propelling our thoughts and actions – is simply too destabilizing. The simulacrum proliferates these hyper-rational facades and simulated realities precisely because they defend against having to confront the “forces we pretend to understand.”
The philosopher Jean Baudrillard’s concept of the simulacra, or a copy without an original – a realm where simulations and representations have become more “real” than reality itself – aptly captures the sense of alienation and dislocation that pervades contemporary culture. In this world of surfaces and appearances, the depth of human experience is often lost, and the quest for authentic meaning becomes increasingly elusive.
Main Ideas and Key Points:
1. Modern society is characterized by hyper-rationality and fragmented meanings, leading to a sense of alienation and confusion.
2. The breakdown of traditional meaning-making systems has left individuals vulnerable to direct encounters with archetypal forces.
3. Jean Baudrillard’s concept of simulacra describes a world of detached images and representations that have replaced authentic reality.
4. Gilbert Durand’s concept of the imaginary suggests that the fragmentation of symbolic coherence contributes to the crisis of meaning.
5. The proliferation of images in contemporary culture leads to information overload and semiotic confusion.
6. T.S. Eliot’s “The Waste Land” reflects the shattered psyche of a post-war generation struggling to find coherence and purpose.
7. Henri Bergson’s ideas on intuition and lived time (durée) offer an alternative to spatialized, quantified conceptions of time.
8. Friedrich Nietzsche viewed science and philosophy as unconscious projections of psychological struggles onto the world.
9. Walter Benjamin’s concept of “shock experience” relates to the traumatization of the modern psyche due to constant stimuli.
10. The emergence of conspiracy theories can be seen as a manifestation of a collective yearning for coherent narratives.
11. James Hillman’s “Re-Visioning Psychology” emphasizes the importance of soul, imagination, and archetypal dimensions in psychology.
12. David Tacey’s concept of the “post-secular sacred” suggests a new understanding of spirituality that transcends the religious-secular dichotomy.
13. Psychotherapy needs to evolve to help patients cultivate intuition and inner wisdom rather than intellectual mastery.
14. The goals of psychotherapy should shift from problem-solving to helping patients develop resilience and adaptability in an uncertain world.
15. Therapy should focus on helping individuals face the unknown with courage, curiosity, and compassion.
16. The interplay of conscious and unconscious intuition is crucial in the therapeutic process.
17. Therapists need to acknowledge their own uncertainties and develop a new kind of post-secular faith in the intuitive process of sense-making.
Appearance of the Unreal
The simulacrum is a conceptual framework proposed by the philosopher and cultural theorist Jean Baudrillard in his book “The Intelligence of Evil or the Lucidity Pact” (2005). It refers to the realm of images and representations that have become detached from reality and taken on a life of their own in contemporary culture.
According to Baudrillard, in the postmodern era, images and simulations have become more real than reality itself. Images circulate and multiply, creating a hyper reality that replaces the real world. In this realm, images no longer represent or refer to an external reality but instead become self-referential and self-generating.
Some key characteristics of the simulacra as described by Baudrillard:
It is a realm of simulacra, where copies and simulations have replaced the original and the authentic.
It is a world of appearances and surfaces, where depth and meaning have been lost.
It is a realm of fascination and seduction, where images captivate and manipulate the viewer.
It is a world of illusion and virtuality, where the boundaries between the real and the imaginary have collapsed.
The simulacra describes a semiotic vertigo, a self-referential hall of mirrors in which signifiers endlessly circulate and proliferate, unmoored from any ultimate signified or referent in material reality. It is a world that has become untethered from the symbolic order, that transcendent horizon of meaning and metaphysical grounding which allows a culture to orient human experience within a coherent frame.
For Baudrillard, the implications of this unraveling of the symbolic order are profoundly disorienting and alienating. The perpetual bombardment of images and spectacle produces a crisis of meaning and a loss of critical distance. Signs and representations become unhinged from the tangible contexts and embodied human narratives that could imbue them with authenticity and significance.
Gilbert Durand’s Imaginary
Gilbert Durand’s concept of the imaginary, as described in his book “The Anthropological Structures of the Imaginary” (1960), can provide valuable insights into the crisis of meaning in the postmodern world. Durand argues that the human imagination is structured by fundamental archetypal patterns that shape our understanding of the world.
For Durand, the realm of images, symbols, and myths constitutes the collective imaginary of a culture, providing a symbolic framework through which individuals can navigate the complexities of existence. However, in the postmodern era, the traditional symbols and myths that once anchored the imaginary have been eroded by the forces of secularization, rationalization, and technological change. The result is a fragmentation of the imaginary, a loss of symbolic coherence that leaves individuals adrift in a sea of disconnected images and meanings.
Durand suggests that the crisis of meaning in contemporary culture is not merely a matter of intellectual or philosophical confusion, but a profound disruption of the archetypal structures that underpin human experience. The challenge, then, is to reconnect with new symbols and myths that can restore a sense of coherence and purpose.
Michel Serres and the Proliferation of Images
Michel Serres, in his work, explores the growing influence of images and visual media in contemporary society. He argues that the proliferation of images has created a new kind of environment that shapes our perception, knowledge, and behavior. Serres’s perspective highlights the way in which images and simulations have come to dominate contemporary culture. The endless circulation of images creates a sense of information overload and semiotic confusion, making it difficult for individuals to discern what is real and what is illusory.
In this context, the task of therapy becomes one of helping patients navigate the world of images, to find ways of grounding their experience in authentic human relationships and chosen, not preprogrammed, narratives. This may involve a critical interrogation of the images and representations that shape our understanding of the world, as well as a renewed emphasis on the importance of symbolic meaning and archetypal structures.
The simulacrum is not merely a philosophical or semiotic problem, but a profound existential challenge. It undermines the very foundations of human subjectivity, calling into question the assumptions and beliefs that have traditionally provided a sense of order and purpose to human experience.
In this context, the role of therapy becomes one of helping patients to confront the radical uncertainty and ambiguity of the postmodern condition. This may involve a willingness to embrace the inherent contradictions and paradoxes of existence, to find meaning in the midst of chaos and confusion.
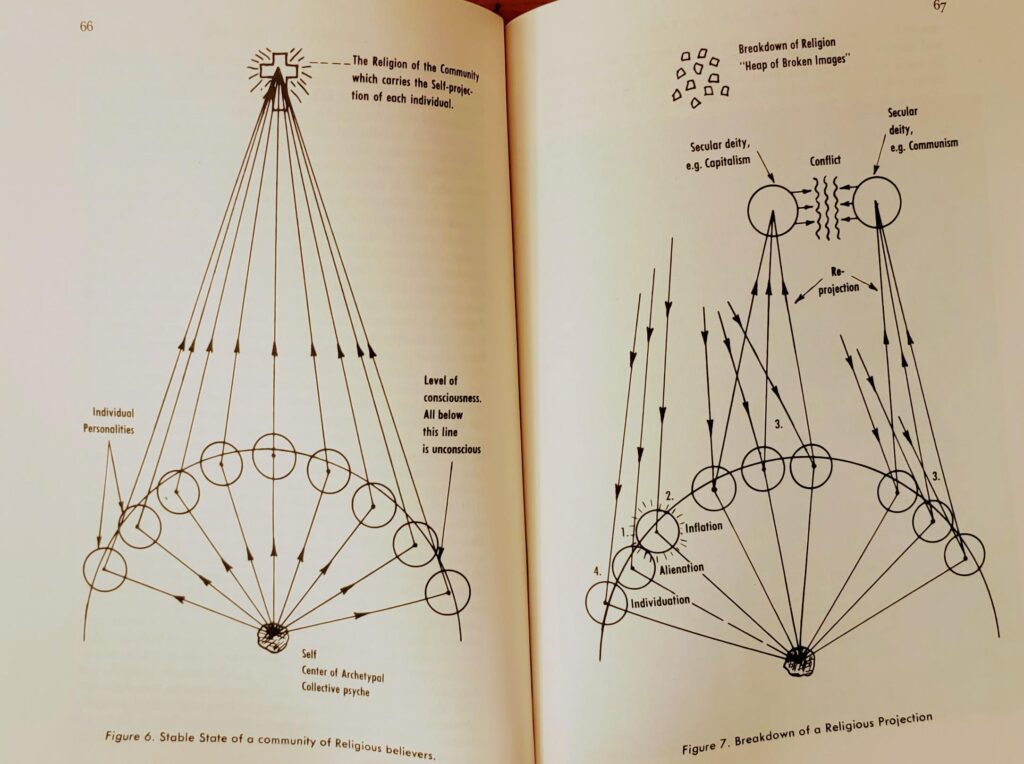
A Heap of Broken Images in the Waste Land of the Modern
The crisis of meaning that haunts the modern age is poignantly evoked in T.S. Eliot’s “The Waste Land.” The poem’s fragmented structure and kaleidoscopic imagery reflect the shattered psyche of a post-war generation, struggling to find coherence and purpose in a world that has lost its moral and spiritual bearings. The “heap of broken images” that Eliot describes is a powerful metaphor for the breakdown of the shared cultural narratives and value systems that once provided a sense of unity and direction to human life.
This theme is echoed in the work of the Jungian analyst Edward Edinger, who argues that the loss of these collective “containers” of meaning has left individuals increasingly vulnerable to the direct impact of archetypal forces. Cut off from the mediating influence of cultural traditions and communal myths, the modern psyche is exposed to the raw power of the unconscious, leading to a range of psychological disturbances, from neurosis and obsession to psychosis and despair.
At the core of the human experience lie archetypal energies, biological drives, unconscious impulses that defy rationalization. The Jungian analyst Edward Edinger highlighted how the breakdown of cultural narratives and societal containers in modernity has left the individual psyche exposed to these primordial currents without adequate symbolic mediation. We are “lived” more by these depths than by the ideological scripts we rehearse on the surface.
The totalizing ideological systems and regimes of image-commodification so pervasive in late capitalism can be viewed as anxious attempts to reinstall order and stuff the denied “forces” back into an old and broken symbolic container. But as Auden intuited, and as the desolation of “The Waste Land” gives voice to, such efforts are doomed to fail in reinstating an authentic sense of meaning and rootedness.
What is required is a re-enchantment of the world, a resacrilization of existence that can hold the tensions of the rational and irrational, the structured and the chaotic, in productive paradox. Rather than defensive pretense, the goal becomes to live into the mysteries with humility and openness. Only by greeting “the forces we pretend to understand” with vulnerability and courage can we hope to restore the symbolic depths modernity has paved over with hyper-rational simulations and spectacles.
The Jungian idea of the tension of the opposites can help us make sense of the dichotomy between the real we we are seeing and the unreal that we are feeling. By trying to pick between these forces we have to pick between either feeling crazy and acting sane or feeling sane and acting crazy. If we are able to feel the truth of both the real an unreal, subjective and objective tension that the cognitive dissonance of the modern era is causing it will become a powerful intuition. This powerful intuition was something harnessed by the theorists and writers mentioned in this essay. It is why their work feels so true even where it might seem on the surface like madness.
Such an approach does not abandon logic, analysis and differentiated understanding. Rather, it balances these with an embrace of ambiguity, a readiness to engage the symbolic potencies of the unconscious, myth and the mysteries that exceed rational categorization. The Buddhist notion of the “still point” that so haunts “The Waste Land” evokes this posture of dwelling in the creative spaciousness between conceptual fixities.
For Jung, it is only through metabolizing psychic opposition that true depth and wholeness can arise. The reconciliation of conflicts within honors psyche’s inexhaustible fertility, rather than defensively walling meaning off within cardboard ideological constructs.
Real and Unreal Time
Henri Bergson wrote that lived time (durée) is fundamentally different from the spatialized, quantified conception of time in science. He saw duration as a heterogeneous, interpenetrating flow irreducible to discrete instants. Intuition, rather than intellect, is the faculty by which we can grasp this dynamic continuity of consciousness. In Creative Evolution, Bergson proposed that evolution is driven by an élan vital – an immanent, indivisible current of life that flows through all living beings, giving rise to novelty and creative emergence rather than just gradual, continuous adaptation.
Totalizing ideologies and the “regimes of image-commodification” in late capitalism are anxious attempts to reinstate a sense of order, but are doomed to fail at providing authentic meaning. What is needed is a re-enchantment and resacralization of the world that can hold the paradoxical tensions between rational and irrational, structured and chaotic.
The Jungian notion of the tension of opposites illuminates the dichotomy between the “real” we see and the “unreal” we feel in the modern world. By feeling the truth of both and inhabiting that cognitive dissonance, it can become a powerful intuition – something you argue animates the work of the thinkers and writers you mention.
The goal is to dwell in the “creative spaciousness” between conceptual fixities, balancing differentiated understanding with an openness to ambiguity, unconscious symbolism, and mystery. Metabolizing psychic opposition in this way allows for true wholeness to emerge, honoring the psyche’s deep generativity.
Bergson sits with the same phenomenon as Eddinger. The modern mind, unmoored from traditional cultural and spiritual structures that once provided symbolic mediation and containment of archetypal energies, is more vulnerable to being overwhelmed by unconscious forces in the wake of traumatic rupture. Rebuilding an authentic relationship to meaning after trauma thus requires recovering a sense of anchoring in the living weave of the world’s mystery and hidden coherence beneath the fragmenting onslaught of a hyper-rationalized, dispirited culture.
Magic as Real and Unreal Intuition
Bergson distinguishes between two forms of religious belief and practice: the “static religion” of closed societies, characterized by conformity to established norms and rituals, and the “dynamic religion” of open societies, driven by the creative impetus of mystical intuition.
Within this framework, Bergson sees magic as a primitive form of static religion. He argues that magic arises from an extension of the “logic of solids” – our practical intelligence attuned to manipulating the material world – into the realm of human affairs. Just as we can cause changes in physical objects through our actions, magical thinking assumes that we can influence others and control events through symbolic gestures and incantations.
Fabulation, on the other hand, is the human faculty of myth-making and storytelling. For Bergson, fabulation serves a vital social function by creating shared narratives and beliefs that bind communities together. It is a defensive reaction of nature against the dissolving power of intelligence, which, left unchecked, could undermine social cohesion by questioning established norms and practices.
While Bergson sees both magic and fabulation as grounded in a kind of “fiction,” he does not dismiss them as mere illusions. Rather, he acknowledges their pragmatic value in structuring human life and experience. However, he also recognizes their limitations and potential dangers, especially when they harden into closed, dogmatic systems that stifle individual creativity and moral progress.
In contrast to static religion, Bergson celebrates the dynamic, mystical élan of open religion, which he sees as the highest expression of the creative impulse of life. Mystics, through their intuitive coincidence with the generative source of reality, are able to break through the closed shells of tradition and breathe new vitality into ossified institutions and beliefs.Bergson’s perspective on the creative, evolutionary impulse of life (élan vital) and the role of intuition in connecting with this generative force can provide a compelling lens for understanding the impact of trauma on the human psyche.
In Bergson’s view, intuition is the key to tapping into the dynamic, flowing nature of reality and aligning ourselves with the creative unfolding of life. It allows us to break through the rigid, spatialized categories of the intellect and coincide with the inner durational flux of consciousness and the world.
Trauma, however, can be seen as a profound disruption of this intuitive attunement. The overwhelming, often unspeakable nature of traumatic experience can shatter our sense of coherence and continuity, leaving us feeling disconnected from ourselves, others, and the vital currents of life.
In this state of fragmentation and dissociation, we may turn to various coping mechanisms and defenses that, while serving a protective function, can also further distract us from the healing power of intuition. For example, we may become rigidly fixated on controlling our environment, engaging in compulsive behaviors, or retreating into numbing addictions – all attempts to manage the chaos and terror of unintegrated traumatic memories.
These trauma responses can be seen as a kind of “static religion” writ small – closed, repetitive patterns that provide a sense of familiarity and safety, but at the cost of flexibility, growth, and open engagement with the dynamism of life. They fulfill some of the same functions as the collective myths and rituals Bergson associated with fabulation, but in a constricted, individual way that ultimately keeps us stuck rather than propelling us forward.
Moreover, the energy consumed by these trauma adaptations can leave us depleted and less able to access the vitalizing power of intuition. Instead of flowing with the creative impulse of the élan vital, we become caught in stagnant eddies of reactivity and defense.
However, just as Bergson saw the potential for dynamic, open religion to renew and transform static, closed systems, healing from trauma involves a return to intuitive attunement and a reintegration with the generative flux of life. This may involve working through and releasing the residual charge of traumatic activation, re-establishing a sense of safety and embodied presence, and cultivating practices that reconnect us with the creative wellsprings of our being.
In Jungian psychology, intuition is seen as a function that mediates between the conscious and unconscious realms of the psyche. Conscious intuition involves a deliberate, reflective engagement with the insights and promptings that emerge from our deeper layers of being. It requires an attitude of openness, curiosity, and discernment, as we seek to integrate the wisdom of the unconscious into our conscious understanding and decision-making.
Unconscious intuition, on the other hand, operates below the threshold of awareness, influencing our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in ways that we may not fully comprehend. When we are cut off from a conscious relationship with our intuitive function – as is often the case in the wake of trauma – our unconscious intuitions can become distorted, projected, and misused.
This might manifest as projections, where we unconsciously attribute our own disowned qualities or experiences onto others, leading to interpersonal conflicts and misunderstandings. It could also take the form of acting out, where unintegrated traumatic experiences drive us to engage in compulsive, self-destructive behaviors. Or it might express itself through somatization, where the body carries the unresolved trauma that the conscious mind cannot bear.
As we develop this more conscious relationship with our unconscious intuition, we can begin to discern the difference between reactive, trauma-based projections and genuine intuitive insights. We can learn to trust and follow the deeper wisdom of our psyche, while also maintaining the boundaries and discernment necessary for healthy functioning.
Nietzsche saw logic as a form of insecurity
In his writing Friedrich Nietzsche saw clearly that the philosophical and scientific works of ultra logical men were not dispassionate, rational examinations of truth, but rather deeply personal confessions that reveal the innermost fears, anxieties, and desires of their authors. He saw the most logical minds greatest works as opportunities to psychoanalyze men who could not see the “forces” that lived through them or the ones they had repressed.
Science and philosophy for Nietzsche were merely unconsciously projected psychological struggles onto the world, creating elaborate metaphysical systems and grand narratives that serve to assuage their deepest existential terrors.
There is much truth in this. When I have a radically existential patient that tells that “hell is other people” I know that that person is really telling me that they, themselves, feel like they are in hell. Nietzsche viewed science and philosophy as unconscious projections of psychological struggles onto the world.
Nietzsche argues that the more a philosophical work presents itself as a purely logical, objective analysis, the more it betrays the underlying psychological desperation and spiritual repression of its creator. The grandiose claims to absolute truth and certainty that characterize much of Western philosophy are, for Nietzsche, simply a manifestation of the philosopher’s inability to confront the fundamental chaos, uncertainty, and meaninglessness of existence. By constructing abstract, rationalistic systems that promise to explain and control reality, philosophers seek to impose order and stability on a world that is ultimately beyond their comprehension.
In this sense, Nietzsche sees the history of philosophy as a series of opportunities to eavesdrop while thinkers inadvertently disclose their most intimate fears and longings while claiming to have discovered universal truths. The more a philosopher insists on the logical necessity and objective validity of their system, the more they reveal the intensity of their own psychological needs and the depths of their existential anguish.
The quest for absolute knowable truth and certainty is fundamentally misguided. The fragmentation and uncertainty that characterize the modern world are not problems to be solved through the application of reason, but rather the inevitable consequence of the collapse of the illusions and defenses that have sustained human beings throughout history.
Nietzsche the Therapist
Rather than seeking to impose a pre-existing framework of meaning onto the patient’s experience, the therapist must work to help the individual confront and embrace the fundamental groundlessness of knowable and quantifiable existence. By learning to let go of the need for certainty and control, and by cultivating a sense of openness and creativity in the face of the unknown, the patient can begin to discover a more authentic and empowering way of being in the world.
Just as philosophers have often unconsciously projected their own fears and desires onto the world, so too may therapists be tempted to impose their own beliefs and values onto their patients. When a patient comes in and says, “hell is other people,” they are really telling the therapist that they, themselves, feel like they are in hell.
Ultimately, the task of healing the modern soul requires a willingness to embrace the full complexity and ambiguity of the human condition, to grapple with the shadows and uncertainties that haunt the edges of our awareness. It requires a stance of openness, curiosity, and compassion towards the multiplicity of human experience, and a recognition that our deepest truths often lie beyond the reach of any single theory or perspective.
“The aim of therapy is to help the patient come to a point where he can live with uncertainty, without props, without the feeling that he must conform in order to belong. He must learn to live by his own resources, to stand on his own two feet.”
-Fritz Perls
Walter Benjamin is Shocking
Walter Benjamin wrote in his essay “On Some Motifs in Baudelaire,” “The shock experience which the passer-by has in the crowd corresponds to what the worker ‘experiences’ at his machine.” In a world where the constant barrage of stimuli, the ceaseless flow of images and information, and the relentless pace of change have become the norm, the human sensorium is subjected to a perpetual onslaught of “shocks” that threaten to overwhelm our capacity for conscious reflection and meaningful engagement with the world.
This ubiquitous experience of shock, for Benjamin, is intimately connected to the phenomenon of trauma. In a world where the protective barriers of tradition, ritual, and collective meaning have been eroded, the psyche is left increasingly vulnerable to the impact of events that exceed its capacity for understanding and assimilation. The result is a profound sense of alienation, disorientation, and fragmentation – a kind of pervasive traumatization of the modern soul.
Benjamin’s insights into the relationship between shock, trauma, and the technologization of experience have potential implications for the practice of psychotherapy. They suggest that the task of healing in the modern world must involve more than simply addressing the symptoms of individual psychopathology, but must also grapple with the broader cultural and societal forces that shape the context of psychological suffering.
In a world where the protective barriers of tradition, ritual, and collective meaning have been eroded, the psyche is left increasingly vulnerable to the impact of events that exceed its capacity for understanding and assimilation. This results in a profound sense of alienation, disorientation, and fragmentation – a kind of pervasive traumatization of the modern soul.
It is all too easy for the psychotherapeutic encounter to reproduce the very conditions that contribute to the traumatization of the self. By creating a space of safety, containment, and reflection, the therapist can help the patient to develop the capacity for what Benjamin calls “contemplative immersion” – a mode of engagement with the world that resists the fragmenting and alienating effects of shock that highly logical psychoeducational or cognitive therapy might cause.
For Benjamin, this loss of aura is symptomatic of a broader crisis of experience in modernity. In a world where everything is mediated through the filter of technology and mass media, our capacity for direct, unmediated experience is increasingly eroded. We become passive consumers of a never-ending stream of images and sensations, unable to anchor ourselves in the concrete realities of embodied existence.
From this perspective everyone becomes a potential producer and distributor of images. We can become mindful of the images and sensations of our inner world and understand what we have internalized. This allows us to reject the empty images and symbols we still have allegiance to and to choose what we absorb from culture and what images we can create internally for ourselves.
For Benjamin, the suffering and trauma of individuals cannot be understood in isolation from the broader social, economic, and political forces that we internalize as inner images that effect our experience of an outer world. Therapists who are informed by Benjamin’s ideas may seek to help individuals not only heal from their own traumatic experiences but also to develop a critical consciousness and a sense of agency in the face of collective struggles. This agency in the patient can start with simply acknowledging these realities in therapy as forces that still do effect us.
All Watched Over By Machines Of Loving Grace
In an era where the dominant paradigm asserts that everything can and should be understood through the lens of rigid science and radical logic, we find ourselves grappling with a profound sense of meaninglessness.
The emergence of conspiracy theories like Q Anon can be seen as a manifestation of our unconscious collective yearning for a coherent narrative that explains the invisible forces that shape our lives. In a world where the true levers of power often remain hidden from view, these folk mythologies provide a sense of order and purpose, even if they are ultimately illusory.
One way to avoid not only destructive conspiracy theories, but also being manipulated by cults and advertisements, is to bring these hidden needs and pains to the surface of the psyche in therapy. If we make them know to ourselves they will not be able to hijack our emotional systems and manipulate our behavior. Viewing ourselves as purely rational and intellectual beings is what leaves these drives for comprehension, stability, inclusion, importance and purpose ripe for exploitation.
Overly cognitive or intellectual therapy can leave these forces dormant as well or worse repress them further beneath the surface of the psyche. As Adam Curtis critiqued in the documentary “All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace,” the notion that humans are merely computers that can be programmed and optimized is a seductive but ultimately flawed worldview. If we think that we are computers then will be driven mad by the dreams within us that cannot find expression through a binary choice.
In the face of this existential uncertainty, psychotherapy must evolve to help patients cultivate a different kind of knowledge—one that is rooted in intuition and inner wisdom rather than intellectual mastery. This is not to say that we should abandon empiricism altogether, but rather that we must recognize its limitations and embrace a more humble, open-ended approach to understanding ourselves and the world around us.
The poem “All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace” by Richard Brautigan, which inspired Curtis’s documentary, envisions a future where humans and nature are harmoniously integrated with technology. While the poem’s utopian vision may seem naive in retrospect, it speaks to a deep longing for a world in which we are not alienated from ourselves, each other, and the natural world. In the context of psychotherapy, this means helping patients to cultivate a sense of connection and meaning that transcends the narrow confines of intellectual understanding.
All Watched Over By Machines Of Loving Grace
I like to think (and
the sooner the better!)
of a cybernetic meadow
where mammals and computers
live together in mutually
programming harmony
like pure water
touching clear sky.
I like to think
(right now, please!)
of a cybernetic forest
filled with pines and electronics
where deer stroll peacefully
past computers
as if they were flowers
with spinning blossoms.
I like to think
(it has to be!)
of a cybernetic ecology
where we are free of our labors
and joined back to nature,
returned to our mammal
brothers and sisters,
and all watched over
by machines of loving grace.
-Richard Brautigan
Re-visioning Psychology
James Hillman, a prominent post-Jungian thinker, presented a radical re-envisioning of psychology in his seminal work, “Re-Visioning Psychology” (1975). His main arguments challenged the prevailing assumptions of modern psychology and proposed a new approach rooted in the imagination, mythology, and the archetypal dimensions of the psyche.
The “Soul” as Central:
Hillman argues for a psychology centered on the “soul,” which he understands not as a religious or metaphysical entity, but as a perspective that deepens and “pathologizes” our engagement with life. He critiques modern psychology for reducing the psyche to the ego and neglecting the imaginative, poetic, and mythic dimensions of experience.
Archetypal Psychology:
Drawing on Jung’s concept of archetypes, Hillman proposes an “archetypal psychology” that sees the psyche as inherently plural and polytheistic. He argues that psychological experiences and symptoms are best understood as expressions of archetypal patterns and images, rather than as personal pathologies to be cured.
The Primacy of Image:
For Hillman, the image is the primary mode of psychic reality. He emphasizes the need to attend to the autonomous, living images of the psyche – as expressed in dreams, fantasies, and symptoms – rather than reducing them to concepts or interpreting them in literal, personalistic terms.
Pathologizing:
Hillman challenges the medical model of psychology, which sees psychological distress as a disorder to be eliminated. Instead, he advocates for a “pathologizing” approach that honors the soul’s need for depth, complexity, and engagement with the full range of human experience, including suffering and shadow aspects.
Psyche as Story:
Hillman sees the psyche as inherently narrative and mythic. He argues that we need to engage with the archetypal stories and patterns that shape our lives, rather than trying to “cure” or “solve” them. This involves cultivating a poetic, imaginative sensibility that can embrace paradox, ambiguity, and the unknown.
Ecological Sensibility:
Hillman’s psychology is deeply ecological, recognizing the interdependence of psyche and world. He argues that psychological healing must involve a reconnection with the anima mundi, the soul of the world, and a re-ensouling of our relationship with nature, culture, and the cosmos.
Critique of Individualism:
Hillman challenges the modern ideal of the autonomous, self-contained individual. He sees the psyche as inherently relational and context-dependent, shaped by the archetypes, myths, and collective patterns of the culture and the wider world.
Throughout “Re-Visioning Psychology,” Hillman argues for a psychology that is poetic, imaginative, and soulful, one that can embrace the full complexity and mystery of the human experience. His work has been influential in the fields of depth psychology, ecopsychology, and the humanities, offering a rich and provocative alternative to the dominant paradigms of modern psychology.
The days of psychoanalysis, which sought to dissect every aspect of the psyche in an attempt to achieve total comprehension, are indeed over. Instead, mental health professionals must focus on helping patients to be at peace with uncertainty and to develop the resilience and adaptability needed to navigate an ever-changing world. This requires a shift away from the pursuit of mastery and control and towards a more fluid, dynamic understanding of the self and the world.
The Post Secular Sacred:
In his book “The Spirituality Revolution: The Emergence of Contemporary Spirituality” (2004), David Tacey, an Australian scholar in the fields of spirituality, religion, and depth psychology, presents a compelling argument about the emergence of a “post-secular sacred” in contemporary culture.
Tacey observes that while traditional religious institutions and beliefs have declined in the modern West, there has been a simultaneous resurgence of interest in spirituality, particularly among younger generations. He argues that this “spirituality revolution” represents a shift towards a new, post-secular understanding of the sacred that transcends the dichotomy between religious and secular worldviews.
Critique of Secular Materialism:
Tacey argues that the dominant paradigm of secular materialism, which reduces reality to the objectively measurable and dismisses the spiritual dimension of life, is inadequate for meeting the deep human need for meaning, purpose, and connection. He sees the rise of contemporary spirituality as a response to the existential emptiness and ecological crisis engendered by a purely materialistic worldview.
Re-enchantment of the World:
Drawing on the work of thinkers such as Carl Jung, Mircea Eliade, and Thomas Berry, Tacey argues for a re-enchantment of our understanding of the world, one that recognizes the presence of the sacred in nature, the cosmos, and the depths of the psyche. He sees this as a necessary corrective to the modern disenchantment of the world, which has led to a sense of alienation, meaninglessness, and ecological destruction.
The Sacredness of the Ordinary:
Tacey emphasizes the importance of discovering the sacred in the midst of everyday life, rather than solely in the context of religious institutions or transcendent experiences. He argues for a democratization of the sacred, where individuals can cultivate a sense of the numinous in their relationships, work, creativity, and engagement with the natural world.
Spirituality as a Developmental Process:
Drawing on the work of psychologists such as Jean Piaget and James Fowler, Tacey presents spirituality as a developmental process, one that unfolds in stages from childhood to adulthood. He argues that the emergence of post-secular spirituality represents a new stage in this process, characterized by a more integrative, pluralistic, and ecologically conscious understanding of the sacred.
Engaging with the Shadow:
Tacey emphasizes the importance of engaging with the shadow aspects of spirituality, such as the potential for spiritual narcissism, escapism, or the abuse of power. He argues for a grounded, embodied spirituality that integrates the light and dark aspects of the psyche and is committed to ethical action in the world.
Ongoing Dialogue between Spirituality and Religion:
While affirming the value of post-secular spirituality, Tacey also recognizes the ongoing importance of traditional religious traditions as sources of wisdom, community, and ethical guidance. He advocates for a dialogue between contemporary spirituality and religion, one that can lead to a mutual enrichment and transformation.
Post-Jungian thinkers who have advocated for a “post-secular sacred” have argued for a kind of scientific empiricism that is infused with a sense of humility, wonder, and openness to the unknown. This perspective recognizes that there are limits to what we can know and understand, but it also affirms the value of subjective experience and the power of intuition and imagination.
In practice, this could lead to new forms of psychoeducation and therapy that emphasize the cultivation of inner wisdom, self-compassion, and a sense of connection to something larger than oneself. Rather than striving to achieve perfect understanding or control, patients would be encouraged to embrace the inherent uncertainty of life and to find meaning and purpose in the present moment.
This is no easy task for therapists. To be truly helpful guides on this path, we must have the honesty to admit that we too are adrift in a sea of uncertainty and fragmented narratives. The solid ground of empirical certitudes and secular meaning systems has receded, leaving us to navigate by situational awareness and intuition. Instead, we must develop a new kind of post-secular faith – not in final truths, but in the intuitive process of sense-making itself.
We, as therapists, must be honest with patients, but in doing so we run the risk of seeming stupid, unqualified or crazy. We don’t know how to do this as therapists either. We don’t have to know how but we have to develop the, perhaps post secular, faith that we can and the intuition to know in which directions to go. We must do all of this in a culture that gives us nothing but uncertainty and heaps of broken images.
New Goals for Therapy
The goals of psychoanalysis are now waiting and new goals must be determined for psychotherapy. The cognitive revolution has done so much damage putting all emphasis on changing external behavior and putting no emphasis on internal inside or capacity for reflection and the ability to “hold the energy” of being human.
One thing that I try and prepare patients for as a psychotherapist is that when they get what they want out of therapy, when their behavior changes are they accomplished some goal, they won’t be happy. People don’t believe me they tell me how if they could just do this or just do that everything would be better.
I have patients that want to get a job, want to move out from living with their parents, want to learn how to be in a relationship, want to attain friendships, a higher salary, any number of things. When they actually do accomplish these goals they realize that the emotions and the hurt and frustration that made these things seem so unattainable are still there even after those things have been attained.
My point is that psychotherapy is a process of growth and that when you get what you want you don’t feel better because you’ve grown and you now have a new goal. We need to deal with the way that we feel and the restlessness that not having the goal creates. These are the tensions that make us human and the real reason that wee are in therapy.
Viewing psychotherapy as a means to accomplish something is not going to get us anywhere good. We do accomplishing things in therapy, quite a few things, but we have forgotten that was not the point.
For the postmodern self is indeed “lived by forces we pretend to understand.” The archaic currents of archetypal life perpetually destabilize our rational narratives and identities. Yet these are not obstacles to be mastered, but the very raw material and creative thermals we must learn to surf upon. Therapy becomes an art of presencing the interplay of potencies – metabolizing their inexorable unfoldings with radical lucidity and compassion.
Ultimately, the goal of psychotherapy in a post-secular, post-empirical world is not to eliminate suffering or to achieve some kind of final, absolute truth. Rather, it is to help patients develop the capacity to face the unknown with courage, curiosity, and compassion. By embracing a more humble, intuitive approach to mental health, we can help individuals to find meaning and purpose in a world that is always in flux, and to cultivate the resilience and adaptability needed to thrive in an uncertain future.
If you are scratching your head that is fine. I don’t know how either but I still know that we can. I have a faith that I feel is more real than what my intellect allows. The future has always been a copy without an original. The past is built on copies of the inner images that others have externalized consciously or not. All we can learn is to recognize the images inside and outside ourselves to discard the unreal and find the more than real.
Our lives are an interplay of forces and we cannot prevent or defeat that. We can only learn to build behavior and cultural machinery to handle the dynamics of their flow.
We are lived by forces that we pretend to understand. At times these forces seem unbearable or impossible to live with, but we must remember also that these forces exist through us and bring that tension into awareness.
When I spent time as a patient in psychotherapy I encountered a lot of drowning and swimming metaphors from my therapists. Perhaps the seas are too rough now to teach patients to swim. Perhaps we need to teach patients to sail a boat. Together we can build a culture than can sail ships again. Freud thought he was a mechanic fixing the boat engine in the patients head but it is time to forget all that reductive scientific positivism.
We need to remember to breath and remember how to use the wind.
References and Further Reading:
- Baudrillard, J. (2005). The Intelligence of Evil or the Lucidity Pact. Berg Publishers.
- Benjamin, W. (1969). The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction. In H. Arendt (Ed.), Illuminations. Schocken Books.
- Brautigan, R. (1967). All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace. In All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace. The Communication Company.
- Curtis, A. (2011). All Watched Over by Machines of Loving Grace [Documentary series]. BBC.
- Edinger, E. F. (1984). The Creation of Consciousness: Jung’s Myth for Modern Man. Inner City Books.
- Eliot, T. S. (1922). The Waste Land. Horace Liveright.
- Frankl, V. E. (1959). Man’s Search for Meaning. Beacon Press.
- Jung, C. G. (1968). The Archetypes and the Collective Unconscious (2nd ed.). Princeton University Press.
- Judge, M. S. (2014). Lyrics of the Crossing. Black Ocean.
- Nietzsche, F. (1974). The Gay Science (W. Kaufmann, Trans.). Vintage Books.
- Nietzsche, F. (1989). On the Genealogy of Morals and Ecce Homo (W. Kaufmann & R. J. Hollingdale, Trans.). Vintage Books.
- Romanyshyn, R. D. (2007). The Wounded Researcher: Research with Soul in Mind. Spring Journal Books.
- Tacey, D. (2004). The Spirituality Revolution: The Emergence of Contemporary Spirituality. Routledge.
- Taylor, C. (2007). A Secular Age. Belknap Press of Harvard University Press.
- Yalom, I. D. (1980). Existential Psychotherapy. Basic Books.





0 Comments