Executive Summary: The Neurobiology of ADHD & AuDHD
The Clinical Reality: ADHD is not a “behavioral problem”; it is a neurodevelopmental disorder affecting the Prefrontal Cortex (Executive Function). It is primarily a regulation disorder involving Dopamine and Norepinephrine.
Key Concepts:
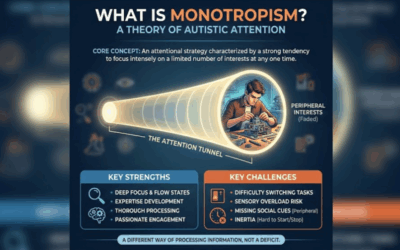
- AuDHD (Autism + ADHD): Up to 50-70% of autistic individuals also present with ADHD. This creates a unique “paradoxical” nervous system that craves novelty (ADHD) while simultaneously needing routine (Autism).
- Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria (RSD): A core, though often undiagnosed, symptom of ADHD involving extreme emotional pain triggered by perceived rejection or failure.
- QEEG Diagnosis: Modern diagnosis moves beyond checklists to look at Theta/Beta brainwave ratios using Brain Mapping.
Clinical Verdict: Treatment requires a “Brain-Based” approach, moving beyond simple talk therapy to interventions that alter neural firing patterns (Neurofeedback, Medication, Somatic Regulation).
Do I Have ADHD? A Deep Dive into Neurodivergence, AuDHD, and Executive Function

For decades, Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) was misunderstood as a condition affecting only “hyperactive young boys.” Today, neuroscience reveals a much more complex picture. ADHD is a lifelong neurobiological difference that affects emotional regulation, motivation, and memory.
Furthermore, recent research has illuminated the massive overlap between ADHD and Autism, leading to the clinical concept of AuDHD. This article explores the biological mechanisms of ADHD, how to screen for it, and how to treat the underlying brain patterns rather than just the symptoms.
Part I: The Neuroscience of the “Interest-Based” Nervous System
The ADHD brain is not “broken”; it is wired differently. Dr. William Dodson describes the ADHD nervous system as Interest-Based rather than Importance-Based.
1. The Prefrontal Cortex and Executive Function
In a neurotypical brain, the Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) acts as the CEO. It regulates attention, inhibits impulses, and organizes future tasks.
In the ADHD brain, the PFC is often underactive (showing excessive Theta waves). This leads to “Executive Dysfunction”—difficulty with starting tasks, switching tasks, and working memory.
2. The Dopamine Deficit
Dopamine is the neurotransmitter of reward and focus. ADHD brains tend to have a lower tonic level of dopamine or a higher density of dopamine transporters (which remove dopamine too quickly).
This forces the ADHD brain to constantly hunt for stimulation (sugar, scrolling, risk-taking) just to bring dopamine levels up to baseline. This is why stimulants (which increase dopamine) help ADHDers feel calmer, not more hyper.
Part II: The Three Presentations of ADHD
The DSM-5 categorizes ADHD into three presentations, though these can fluctuate over a lifetime.
1. Predominantly Inattentive (Formerly ADD)
Often missed in childhood, especially in women.
* Symptoms: Brain fog, daydreaming, sluggish cognitive tempo, forgetfulness, and difficulty processing auditory information.
* The Experience: “I am trying to listen, but the words just slide off my brain.”
2. Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive
The stereotypical presentation, but in adults, it often internalizes.
* Symptoms: Inner restlessness (“motor running”), interrupting others, impulsive spending or eating, inability to relax.
* The Experience: “I feel like I have to be doing something constantly or I will explode.”
3. Combined Type
The most common clinical presentation, involving a mix of executive dysfunction and impulsivity.
Part III: AuDHD (The Autism + ADHD Comorbidity)
Recent studies suggest that 50-70% of Autistic individuals also meet the criteria for ADHD. This specific profile, dubbed AuDHD, comes with unique challenges that standard ADHD advice often fails to address.
The Internal War
The AuDHD brain is a living contradiction:
* The ADHD side: Craves novelty, spontaneity, and high stimulation.
* The Autistic side: Craves routine, predictability, and sensory safety.
* The Result: The individual starts a new hobby (ADHD) and then feels overwhelmed by the change (Autism). Or they plan a rigid schedule (Autism) and feel suffocated by it (ADHD).
Sensory Processing & Burnout
Both ADHD and Autism involve sensory processing differences. The AuDHD individual is highly susceptible to Autistic Burnout—a state of chronic exhaustion caused by masking neurodivergent traits to fit into a neurotypical world.
Part IV: Emotional Regulation and RSD
While not in the DSM, Rejection Sensitive Dysphoria (RSD) is recognized by clinicians as a defining feature of ADHD.
Because the ADHD brain has no “brakes” on emotion, a perceived rejection or failure triggers a catastrophic emotional response. This can look like sudden rage or deep, suicidal despair. Unlike mood disorders (Bipolar), RSD episodes are situational and short-lived, resolving once the trigger is removed.
Part V: Brain-Based Treatment Options
Standard talk therapy is often ineffective for ADHD because you cannot “talk” your Prefrontal Cortex into making more dopamine. We need Brain-Based Medicine.
1. Diagnosis: QEEG Brain Mapping
Before treatment, we use QEEG Brain Mapping to visualize the issue. ADHD brains typically show a high Theta/Beta Ratio—too much slow-wave activity (dreaming) during tasks that require fast-wave activity (focus).
2. Neurofeedback
Neurofeedback trains the brain to reduce excessive Theta waves and increase Beta waves. It is “physical therapy” for the attention networks, offering a non-pharmaceutical way to improve executive function permanently.
3. Medication Management
- Stimulants (Adderall, Vyvanse, Ritalin): Increase dopamine and norepinephrine availability in the synaptic cleft.
- Non-Stimulants (Strattera, Intuniv): Target norepinephrine specifically or alpha-2 receptors to improve emotional regulation and working memory.
4. Somatic & Behavioral Therapy
- DBT (Dialectical Behavior Therapy): Essential for managing RSD and emotional volatility.
- Body Doubling: Working alongside another person to anchor attention (a common strategy in ADHD coaching).
Conclusion: From Deficit to Difference
If you identify with these symptoms, you are not lazy, and you are not broken. You have a high-performance engine with bicycle brakes. With the right support—whether that is medication, neurofeedback, or accommodating your AuDHD needs—you can learn to drive the car.
Explore Neurodivergent Support
Taproot Therapy Collective Podcast
Assessment & Regulation
QEEG Brain Mapping: See Your Brainwaves
Neurofeedback: Training for Focus
Brainspotting: Deep Brain Focus
Emotional & Somatic Support
DBT: Skills for Emotional Regulation
Lifespan Integration: Healing Developmental Trauma
ETT: Visual Stimulation Therapy
Aromatherapy for Sensory Regulation
Scientific Bibliography
- Barkley, R. A. (2012). Executive Functions: What They Are, How They Work, and Why They Evolved. Guilford Press.
- Volkow, N. D., et al. (2009). Motivation deficit in ADHD is associated with dysfunction of the dopamine reward pathway. Molecular Psychiatry.
- Leitner, Y. (2014). The co-occurrence of autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children – what do we know? Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
- Dodson, W. W. (2016). Secrets of the ADHD Brain: Why we think, act, and feel the way we do. ADDitude Magazine.





















0 Comments