Understanding Autism and ADHD (AuDHD): The Overlooked Overlap and Potential of Micronutrient Treatment
Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are two of the most common neurodevelopmental conditions, each with its own set of diagnostic criteria and challenges. However, there is a significant overlap between these disorders that is often overlooked, leading to misdiagnosis or inadequate treatment. This co-occurrence is sometimes referred to as AuDHD.
In this article, we’ll explore the signs and symptoms of AuDHD, the diagnostic challenges, and take an in-depth look at the emerging evidence for broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas in managing these complex conditions.
What does AuDHD feel like?
The Overlap Between Autism and ADHD
Studies suggest that up to 50-70% of individuals with ASD also meet the criteria for ADHD, and vice versa [1]. This overlap, or AuDHD, is characterized by a combination of core features from both disorders:
- Social communication difficulties and restricted, repetitive behaviors from ASD
- Inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity from ADHD
- Shared challenges with executive function, sensory processing, and emotional regulation
Despite this high comorbidity, AuDHD is not a formal diagnosis in the DSM-5. Individuals may receive separate diagnoses of ASD and ADHD, or have one condition missed entirely. This diagnostic complexity can delay appropriate interventions.
How to know if you have AuDHD
Diagnostic Challenges and Barriers to Recognition
Several factors contribute to the under-recognition of AuDHD:
Overshadowing:
The more impairing condition (often ASD) may overshadow or mask symptoms of the other. Providers may attribute ADHD-like symptoms to autism alone.
Diagnostic criteria:
DSM-5 criteria for ASD and ADHD don’t capture the nuanced overlap and interaction between the conditions. Rigid cut-offs may exclude some affected individuals.
Age of diagnosis:
ASD is often diagnosed in early childhood, while ADHD may not be identified until later. Early autism diagnoses may not fully consider co-occurring ADHD.
Compensatory strategies:
Highly intelligent individuals with AuDHD may develop coping mechanisms that disguise their struggles, leading to missed or late diagnosis.
Lack of provider training:
Not all mental health professionals are adequately trained in recognizing and treating the complex presentation of AuDHD.
Stigma and misconceptions:
Stereotypes about autism and ADHD being distinct disorders may cloud clinical judgment and limit consideration of co-occurrence.
Overcoming these barriers requires a more dimensional, multi-level approach to assessment that considers the full range of an individual’s strengths and challenges. Comprehensive evaluations using validated tools, detailed developmental history, and observations across settings are essential.
The Potential of Micronutrients for Managing AuDHD
Given the diagnostic and treatment complexities of AuDHD, novel approaches targeting underlying physiological factors hold promise. One such approach is the use of broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas, which provide therapeutic doses of essential vitamins, minerals, and amino acids to support optimal brain function.
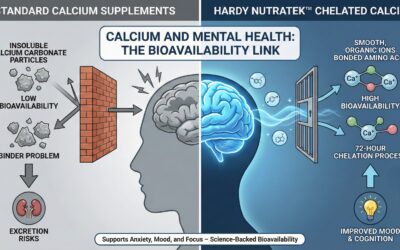
Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients is a leading example of a comprehensive micronutrient blend that has been extensively studied for mood and neurodevelopmental disorders. It contains a carefully balanced array of over 40 nutrients, including:
- High-dose B-vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B12, folate): Critical for neurotransmitter synthesis, methylation, and energy production. Deficiencies are common in ASD and ADHD [2].
- Antioxidants (vitamins A, C, E, zinc, selenium): Protect brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation, which are elevated in AuDHD [3].
- Vitamin D: Regulates serotonin synthesis, immune function, and gene expression. Low levels linked to ASD and ADHD symptoms [4].
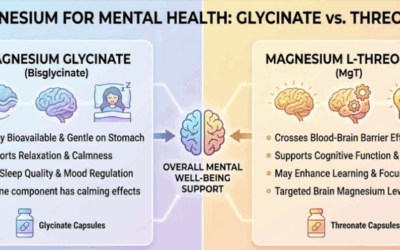
- Magnesium: Modulates NMDA glutamate receptors and supports relaxation. Deficiency associated with hyperactivity and anxiety [5].
- Zinc: Cofactor for 100+ enzymes, influences GABA and glutamate, regulates dopamine transport. Deficits found in ASD and ADHD [6].
- Iron: Essential for dopamine synthesis and myelination. Low levels linked to ADHD [7].
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Building blocks for neuronal membranes, regulate inflammation, support synaptic plasticity. Promising intervention for AuDHD [8].
- Amino acids (taurine, glutamine, methionine): Neurotransmitter precursors, sulfur donors, antioxidants. Abnormalities seen in ASD [9].
- Botanicals (ginkgo biloba, grape seed, acetyl-L-carnitine): Enhance cerebral blood flow, provide polyphenols, and mitochondrial support. May improve ASD and ADHD symptoms [10].
By supplying a comprehensive complement of brain-essential nutrients in bioavailable forms and research-backed doses, micronutrient formulas like Daily Essential Nutrients target multiple mechanisms implicated in AuDHD:
Neurotransmitter Modulation
Micronutrients provide cofactors and precursors for synthesizing monoamines (serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine), GABA, and other neurotransmitters that regulate mood, attention, impulse control, and social behavior – core domains affected in AuDHD.
B6, iron, and amino acids are needed to produce serotonin, which is essential for social communication [11]. B12, iron, and folate drive dopamine synthesis, with deficiencies linked to ADHD [12]. Vitamin D enhances serotonin release and regulates dopamine turnover [13].
Magnesium and zinc modulate NMDA glutamate receptors, which are overactive in both ASD and ADHD, contributing to excitotoxicity, hyperactivity, and anxiety [14]. Taurine and omega-3s also stabilize glutamate signaling [15].
Neuroprotection and Plasticity
Oxidative stress and neuroinflammation are well-documented in AuDHD, disrupting brain development and function [16]. The combination of antioxidant vitamins (A, C, E), minerals (selenium, zinc, manganese), and plant compounds (ginkgo, grape seed) in micronutrients scavenges free radicals and enhances the body’s detoxification capacity.
Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, magnesium, and B-vitamins also reduce neuroinflammation by modulating immune cells and inflammatory pathways in the brain [17]. This may help normalize microglial pruning and protect against neuronal damage.
Nutrients like zinc, choline, vitamin D, and omegas support neuronal membrane structure, myelination, and synaptic plasticity – essential for learning, memory, and behavioral flexibility [18]. Acetyl-L-carnitine delivers fatty acids to mitochondria to power neuronal energy production.
These neuroprotective and neuromodulatory effects may enhance the brain’s capacity for growth and adaptation, which is often compromised in AuDHD.
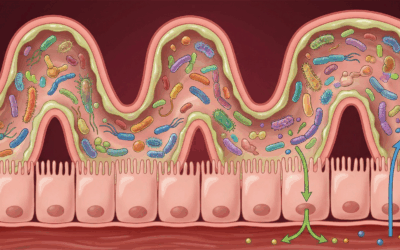
Gut-Brain Axis and Microbiome
The microbiome-gut-brain axis is increasingly recognized as a key player in neurodevelopment [19]. Children with AuDHD often exhibit altered gut microbiota, intestinal permeability, and gastrointestinal symptoms that can exacerbate behavioral issues [20].
Micronutrients support gut health by providing prebiotics (fiber), amino acid fuel, and cofactors for a balanced microbiome. B-vitamins, zinc, betaine, and folate assist in repairing the gut lining and preventing “leaky gut.” Probiotics in formulas deliver beneficial bacteria.
A healthy microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids (butyrate, acetate) that epigenetically regulate brain development, as well as neurotransmitters like serotonin and GABA [21]. Correcting dysbiosis and gut-derived inflammation may improve mood, cognition, and immune function.
Epigenetics and Neurogenetic Pathways
Nutrients are essential cofactors for one-carbon metabolism and DNA methylation, which epigenetically control gene expression related to neurodevelopment, stress response, and synaptic plasticity – pathways implicated in the etiology of AuDHD [22].
Folate, B12, B6, choline, and zinc are methyl donors and enzymatic cofactors for DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs). Vitamin A, D, and selenium influence histone modifications and chromatin remodeling [23].
Adequate supply of these epigenetic nutrients, especially during critical developmental windows, may optimize gene expression patterns and compensate for genetic susceptibilities common in AuDHD, such as polymorphisms in MTHFR, COMT, and dopamine receptor genes [24].
The ultimate goal of micronutrient therapy is to correct underlying biochemical imbalances and deficiencies that contribute to the neurodevelopmental abnormalities in AuDHD, setting the stage for clearer improvements from behavioral and educational interventions. While not a complete substitute for medication in all cases, micronutrient formulas may offer a favorable option for some individuals seeking a lower-risk, integrative approach.
Clinical Evidence for Micronutrients in AuDHD
Several clinical trials and case reports have documented benefits of broad-spectrum micronutrients for both ASD and ADHD symptoms:
For ASD:
- A randomized, placebo-controlled trial in 141 children and adults with ASD found that vitamin/mineral supplementation for 12 weeks significantly improved symptoms of hyperactivity, tantrums, overall and receptive language, and behavior, with greater benefits seen in those with more severe symptoms at baseline [25].
- An open-label pilot study of a similar micronutrient formula in 11 children with ASD reported significant improvements in ASD symptoms, verbal communication, hyperactivity, and restricted interests after 2-6 months, which were maintained at follow-up [26].
- Case studies describe dramatic reductions in tantrums, aggression, self-injurious behaviors, and improvements in mood, attention, language, and social engagement in children with ASD taking Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients long-term [27].
For ADHD:
- A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 93 medication-free children aged 7-12 with ADHD found that 10 weeks of Daily Essential Nutrients micronutrients significantly reduced inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity compared to placebo, with effect sizes similar to medications. 54% of micronutrient group showed at least 30% decrease in ADHD symptoms [28].
- A case series of children and teens with ADHD treated with Daily Essential Nutrients for 6-12 months found that over 70% experienced “much” or “very much” improvement in ADHD symptoms, mood, and anxiety, based on clinician rating scales [29].
- An RCT in 80 adults with ADHD showed greater improvement in inattention and hyperactivity for those taking a broad-spectrum formula compared to placebo over 8 weeks, with 38% showing at least 30% decrease in symptoms [30].
While research on micronutrients for specifically diagnosed AuDHD is currently lacking, the positive findings for each condition separately suggest potential for this comorbid population. Larger RCTs with long-term follow-up, and head-to-head comparisons with standard medications, will help further clarify optimal use.
Safety and Practical Considerations
Broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas like Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients appear generally well-tolerated, with no reports of serious adverse effects in the published studies. Most common side effects are mild and transient GI symptoms like nausea or loose stools [31].
rients as part of a personalized, integrative treatment plan for AuDHD. More research is still needed to refine optimal dosing, long-term effects, and direct comparisons with medications.
As always, consult with a qualified healthcare provider knowledgeable about AuDHD and nutrition to determine if micronutrient therapy may be suitable for your specific situation. With greater awareness and a holistic, evidence-based approach, individuals with AuDHD can harness their strengths and thrive.
Note: This article provides educational information and is not intended as medical advice. Broad-spectrum micronutrient formulas like Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients are classified as dietary supplements and do not have regulatory approval for treating AuDHD. Consult your doctor before starting or changing any therapies. Individual results may vary.
Special Offer and Disclaimer
Special Offer
Learn more about how micronutrituib can treat mental health Issues.
As a thank you to our readers, you can get 15% off your first order of Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients by using code TAPROOT at www.hardynutritionals.com. Offer valid for new customers only. Always consult your healthcare provider first to determine if micronutrient supplementation is appropriate for your individual needs. We recieve a small comission on sales.
Disclaimer: Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients is a dietary supplement intended to provide nutritional support for overall health and is not a replacement for standard AuDHD medical treatment or medication. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease. Consult your physician prior to starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you are taking medications or have a medical condition. This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Hardy Daily Essential Nutrients is a dietary supplement and not a replacement for standard ADHD treatments. Always consult with your doctor before starting or changing any therapies. Results may vary.
References
[1] Johnstone, J. M., Hatsu, I., Tost, G., Srikanth, P., Eiterman, L. P., Bruton, A. M., … & Arnold, L. E. (2022). Micronutrients for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in youth: A placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 61(5), 647-658.
[2] Stevens, A. J., Purcell, R. V., Eggleston, M. J. F., & Rucklidge, J. J. (2020). A Micronutrient Intervention for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children and Adolescents: Clinical Observations in an Open-Label Case Series. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 30(10), 630-638.
[3] Rucklidge, J. J., Frampton, C. M., Gorman, B., & Boggis, A. (2014). Vitamin-mineral treatment of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in adults: double-blind randomised placebo-controlled trial. The British Journal of Psychiatry, 204(4), 306-315.
[4] Zhu, X., Zhang, Y., Zhou, Q., Wu, C. D., Arslan, D., Yang, F., … & Du, Y. (2022). Efficacy of vitamin and mineral supplements for reducing aggression and rule-breaking behaviors in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 1-16.






















0 Comments