Navigating the Complexities of Emotion: Insights from a Psychotherapist
As a psychotherapist, one of the most common challenges I see clients face is understanding and managing their emotions. Emotions play a crucial role in our daily lives, influencing our thoughts, behaviors, and overall well-being. In this article, we’ll explore the three basic negative emotions – anger, sadness, and fear – and discuss effective strategies for working with them.
The Three Basic Negative Emotions
Before we dive into strategies for managing emotions, let’s take a closer look at the three basic negative emotions and what they can tell us about our internal world.
Anger
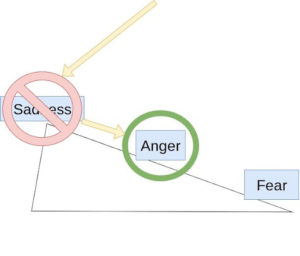
Anger arises when we feel that one of our rules or boundaries has been violated [1]. It’s a more adaptable state than fear because it requires believing that we have some control over our reality and a right to have rules and boundaries. When anger is unavailable as a state, we may revert to fear.
Some common signs of anger include:
- Feeling hot or flushed
- Clenching jaw or fists
- Rapid heartbeat
- Tense muscles
- Irritability or frustration
Sadness
Sadness is the most adaptable state, requiring us to be in touch with our own vulnerability and have faith in our capacity for healing [2]. It allows us to accept events outside of our control. Without the ability to feel sadness, we may resort to anger to maintain control.
Some common signs of sadness include:
- Feeling heavy or fatigued
- Crying or tearfulness
- Loss of interest in activities
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in appetite or sleep
Fear
Fear is the absolute flight state, characterized by a sense of powerlessness and hopelessness [1]. It is the least adaptable state, where we feel that we have no control over our reality and that the world may hurt us.
Some common signs of fear include:
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Trembling or shaking
- Feeling cold or numb
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Strategies for Managing Emotions
Now that we have a better understanding of these basic negative emotions, let’s explore some effective strategies for managing them.
1. Identify the Emotion
The first step in managing emotions is to identify what you’re feeling [3]. Is it anger, sadness, or fear? Acknowledging the emotion is crucial in addressing it effectively. Take a moment to check in with yourself and notice what’s coming up for you.
2. Allow Yourself to Feel
Once you’ve identified the emotion, allow yourself to feel it without judgment [4]. Notice how it affects your thoughts and body. Are there physical sensations like tightness, coldness, or changes in heart rate? Giving yourself permission to experience the emotion fully can paradoxically help it pass through more quickly.
3. Explore the Roots
Create an “I” statement that explains why you feel the emotion [1]. This should focus on how something or someone’s behavior affected you, rather than judging them. For example, “I feel angry when my boundaries are crossed” or “I feel sad when I don’t feel seen or understood.” Understanding the reason behind your emotions can help you address the underlying issues.
4. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help you stay present and manage your emotional responses [5]. By focusing on the present moment, you can reduce the intensity of negative emotions and gain clarity. Some simple mindfulness practices include:
- Focusing on your breath
- Doing a body scan
- Observing your thoughts without getting caught up in them
- Engaging your senses (e.g., noticing sights, sounds, smells)
5. Seek Professional Help
If you find it challenging to manage your emotions on your own, don’t hesitate to seek the guidance of a psychotherapist [6]. They can help you develop personalized strategies for understanding and regulating your emotions. Some effective therapeutic approaches for working with emotions include:
- Emotion-Focused Therapy (EFT)
- Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
- Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
- Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
- Sensorimotor Psychotherapy
Remember, seeking professional help is a sign of strength and self-awareness, not weakness.
Conclusion
Emotions are a natural part of the human experience, and learning to understand and manage them is essential for our mental health and well-being. By identifying your emotions, allowing yourself to feel them, and exploring the reasons behind them, you can develop greater emotional resilience and adaptability.
If you’re interested in doing some self-therapy work, check out the emotion worksheet we use at Taproot Therapy Collective. This tool can help you gain insight into your emotional patterns and practice the strategies discussed in this article.
Remember, the journey towards emotional well-being is an ongoing process. Be patient and compassionate with yourself as you navigate the complexities of your inner world. And if you need additional support, don’t hesitate to reach out to a qualified psychotherapist.
References
- Greenberg, L. S. (2015). Emotion-focused therapy: Coaching clients to work through their feelings (2nd ed.). American Psychological Association. https://doi.org/10.1037/14692-000
- Neff, K. (2011). Self-compassion: The proven power of being kind to yourself. William Morrow.
- Linehan, M. M. (2015). DBT® skills training manual (2nd ed.). Guilford Press.
- Brach, T. (2004). Radical acceptance: Embracing your life with the heart of a Buddha. Bantam.
- Segal, Z. V., Williams, J. M. G., & Teasdale, J. D. (2012). Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy for depression (2nd ed.). Guilford Press.
- Ecker, B., Ticic, R., & Hulley, L. (2012). Unlocking the emotional brain: Eliminating symptoms at their roots using memory reconsolidation. Routledge.
Additional Resources
- Brown, B. (2010). The gifts of imperfection: Let go of who you think you’re supposed to be and embrace who you are. Hazelden Publishing.
- Ekman, P. (2003). Emotions revealed: Recognizing faces and feelings to improve communication and emotional life. Times Books.
- Gilbert, P. (2009). The compassionate mind: A new approach to life’s challenges. New Harbinger Publications.
- Harris, R. (2008). The happiness trap: How to stop struggling and start living. Trumpeter.
- Ogden, P., Minton, K., & Pain, C. (2006). Trauma and the body: A sensorimotor approach to psychotherapy. W. W. Norton & Company.
- Siegel, D. J. (2010). Mindsight: The new science of personal transformation. Bantam.




















0 Comments