Emerging Research and Clinical Applications for Supplements for Aggression and Anger
Aggression represents a complex behavioral pattern influenced by a multitude of neurobiological, psychological, and environmental factors. While pharmacological interventions remain the standard treatment for pathological aggression, growing evidence suggests that nutritional factors may play a significant role in both the development and management of aggressive behaviors. The Dictionary of Supplements and Herbs for mental health provides valuable insights into how targeted nutritional interventions might help regulate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying aggression.
Neurotransmitter Imbalance and Aggressive Behavior
Aggression has been linked to imbalances in several key neurotransmitter systems, particularly serotonin, dopamine, and GABA. Research published in the Journal of Psychiatric Research has consistently demonstrated an inverse relationship between serotonin levels and aggressive behavior, suggesting that nutrients supporting serotonin synthesis and function may help reduce aggression.
Inositol, a carbocyclic sugar that serves as a precursor for second messengers in serotonin signaling pathways, has shown promise in mood regulation. A study from Tel Aviv University found that inositol supplementation produced improvements in irritability and aggressive outbursts in patients with various mood disorders.
Choline, an essential nutrient that supports the production of acetylcholine, has been implicated in impulse control and aggressive behavior regulation. Research from the University of North Carolina demonstrated that individuals with higher choline intake showed better emotional regulation and reduced reactive aggression on standardized measures.
B Vitamins: Critical Cofactors for Neurotransmitter Synthesis
The B vitamin complex plays a fundamental role in neurotransmitter synthesis and nervous system function. Vitamin B6 serves as a cofactor in the production of serotonin, GABA, and dopamine—all neurotransmitters implicated in aggression regulation.
A landmark study published in Neuropsychobiology found that B6 supplementation reduced aggressive behaviors in a subset of patients with heightened irritability and poor impulse control. This effect was particularly pronounced in individuals with suboptimal B6 status at baseline.
Similarly, niacin (Vitamin B3) supports energy metabolism in brain cells and helps maintain healthy nervous system function. Research from Oxford University has linked niacin deficiency to irritability and aggressive behavioral patterns, suggesting a potential therapeutic role for supplementation in vulnerable populations.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Neural Membrane Function
The role of omega-3 fatty acids in brain function has been extensively studied, with compelling evidence for their involvement in mood regulation and impulse control. A meta-analysis published in the Journal of the American Medical Association found that omega-3 supplementation produced modest but significant reductions in aggressive behavior across diverse populations, including children with conduct disorder and adults with histories of aggression.
The Dictionary of Supplements highlights that omega-3s support neural membrane fluidity and neurotransmitter receptor function, potentially modulating the neurobiological circuits involved in aggression.
Mineral Deficiencies and Behavioral Dysregulation
Several minerals have been implicated in the regulation of aggressive behavior, most notably zinc, magnesium, and iron. Zinc deficiency has been associated with increased irritability and aggressive outbursts, particularly in adolescent populations. A controlled trial published in the Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry demonstrated that zinc supplementation reduced impulsive aggression in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and suboptimal zinc status.
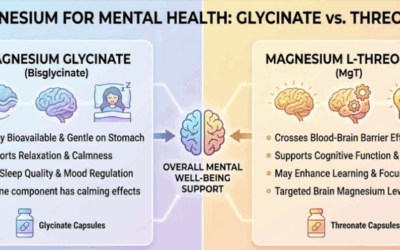
Magnesium, often described as nature’s relaxant, modulates NMDA receptor function and affects stress response systems. Research from the University of Adelaide found that magnesium supplementation reduced aggressive behavior in a residential treatment setting for youth with conduct disorders, with effects persisting throughout the 12-week intervention period.
The inclusion of Great Salt Lake minerals in some comprehensive supplementation protocols may address multiple mineral deficiencies simultaneously, potentially offering broader benefits for behavioral regulation.
Blood Sugar Regulation and Aggressive Behavior
Fluctuations in blood glucose have been linked to irritability and aggressive behavior, particularly in vulnerable individuals. Chromium plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, with research suggesting that it may help stabilize mood by reducing glucose fluctuations.
A study published in Biological Psychiatry demonstrated that chromium supplementation reduced aggressive outbursts and irritability in individuals with atypical depression characterized by carbohydrate craving and mood lability. This effect appeared mediated through improved glucose regulation and related changes in neurotransmitter availability.
Anti-inflammatory Compounds and Neuroinflammation
Emerging research has identified neuroinflammation as a potential contributor to aggressive behavior, suggesting that anti-inflammatory compounds may offer therapeutic benefits. Ginger root extract contains gingerols and shogaols that demonstrate potent anti-inflammatory effects, potentially addressing inflammatory processes that may contribute to aggressive behavior.
Similarly, grape seed extract has shown promise in reducing neuroinflammation through its proanthocyanidin content. A 2023 study in the Journal of Neuroinflammation found that grape seed extract reduced inflammatory markers in the brain and improved behavioral measures in an animal model of aggression.
Adaptogenic Herbs for Stress Regulation
Chronic stress can exacerbate aggressive tendencies, suggesting a potential role for adaptogenic herbs in managing aggression. Eleuthero root has demonstrated effects on cortisol regulation and stress adaptation, potentially moderating the stress response that can trigger aggressive episodes.
Research published in Phytomedicine demonstrated that eleuthero supplementation reduced irritability and improved stress coping in individuals with anxiety disorders characterized by irritable mood. The researchers hypothesized that improved HPA axis regulation might contribute to these behavioral improvements.
Licorice root extract contains compounds that modulate cortisol metabolism, potentially affecting stress-related aggressive responses. However, clinical application requires careful monitoring due to potential effects on blood pressure and electrolyte balance.
Amino Acids and Neurotransmitter Synthesis
Specific amino acids serve as direct precursors to neurotransmitters involved in aggression regulation. Acetyl-L-carnitine has gained attention for its potential to modulate glutamatergic neurotransmission and reduce aggressive behavior.
A clinical trial published in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology found that acetyl-L-carnitine supplementation reduced aggressive behavior and irritability in patients with dementia, suggesting potential applications for other populations with impulsive aggression.
Antioxidants and Neuroprotection
Oxidative stress may contribute to neural circuit dysfunction implicated in aggressive behavior. Alpha-lipoic acid has demonstrated powerful antioxidant effects, potentially protecting neural tissues from oxidative damage.
Research from the University of California suggests that alpha-lipoic acid may help preserve dopaminergic function in regions involved in impulse control and behavioral regulation, offering a potential mechanism for its effects on aggressive behavior in preliminary studies.
Vitamin E provides essential antioxidant protection for neural membranes, with some research suggesting a role in preventing oxidative damage to neurotransmitter systems involved in behavioral regulation. A long-term cohort study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology found an inverse relationship between vitamin E status and measures of hostility and aggression in mid-life adults.
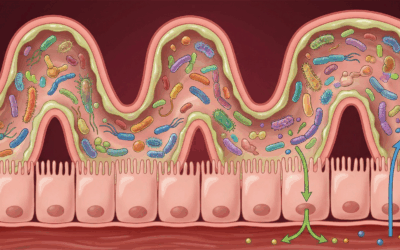
Gut-Brain Axis and Aggressive Behavior
The gut-brain connection has emerged as a critical factor in behavioral regulation, with potential implications for aggressive tendencies. Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains have shown preliminary evidence for reducing irritability and aggressive behavior in some clinical populations.
A fascinating study published in the journal Brain, Behavior, and Immunity demonstrated that probiotic supplementation reduced aggressive thoughts and improved mood in healthy volunteers, potentially through reduced inflammation and improved tryptophan metabolism for serotonin production.
Clinical Applications and Personalized Approaches
The complexity of aggressive behavior necessitates a personalized approach to nutritional intervention. The comprehensive nutritional assessment described in the Dictionary of Supplements provides a framework for identifying individual nutritional imbalances that may contribute to aggressive tendencies.
Clinicians interested in integrating nutritional approaches may consider targeted assessments of B vitamin status, mineral levels, inflammatory markers, and oxidative stress indicators to guide personalized interventions. Collaboration between mental health providers, nutritionists, and primary care physicians offers the most comprehensive approach to addressing the multifaceted nature of pathological aggression.
As research in nutritional psychiatry continues to evolve, the integration of evidence-based nutritional strategies may enhance conventional treatments for aggressive behavior, potentially reducing reliance on pharmacological interventions and improving outcomes across diverse patient populations.
For more information on supplemens for mental health consult our comprehensive guide for micronutrient and supplement therapy and how it can treat specific issues and enhance certain modalities of therapy.
If you’re interested in exploring micronutrient therapy as part of your anxiety treatment plan, Hardy Nutritionals offers a range of products to fit your specific needs. Their Daily Essential Nutrients clinical strength formula provides comprehensive, research-backed dosages in convenient capsule or powder form.
For 15% off in savings, use the offer code “Taproot” at checkout on the Hardy Nutritionals website to receive 15% off your order. @ GetHardy.com
It’s important to remember that while micronutrient therapy can be a powerful tool for managing anxiety, it is not a replacement for professional mental health care. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen, particularly if you have pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
Disclaimer: These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Please consult with a qualified healthcare professional before beginning any supplement regimen, particularly if you are pregnant, nursing, have a medical condition, or are taking medications. The information on this website doesnot constitute medical advice. We recieve a small commision on sales with Hardy Nutritionals through our offer code. Our affiliation does not effect treatment or recomendations made by Taproot authors, therapists or other staff.






















0 Comments