Who was Harry Harlow?
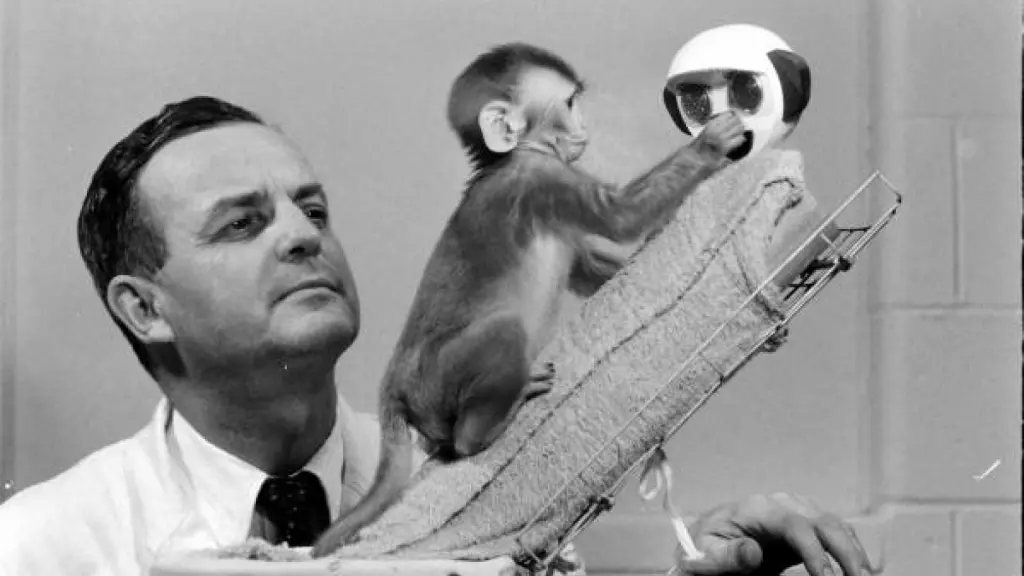

Harry Frederick Harlow (1905-1981) was a groundbreaking American psychologist best known for his seminal work on affection, attachment, and social behavior in rhesus monkeys. His pioneering experiments challenged prevailing theories of the time and reshaped our understanding of the nature and importance of love and emotional bonds in early development. Despite the controversial nature of some of his work, Harlow’s findings have had far-reaching implications for fields ranging from child psychology to animal welfare.
1. Early Life and Academic Career
1.1. Childhood and Education
Harry Harlow was born on October 31, 1905, in Fairfield, Iowa. The third of four sons born to Alonzo and Mabel Harlow, his early life was marked by financial hardship and his father’s frequent absences. Despite initial academic struggles, Harlow excelled in his studies, earning a bachelor’s degree in psychology from Stanford University in 1927 and a Ph.D. in psychology from the same institution in 1930.
1.2. Early Research and Academic Appointments
Harlow began his academic career at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, where he would remain for the rest of his life. Initially focusing on learning and memory in rats and primates, he made significant contributions to the development of the Wisconsin General Test Apparatus (WGTA), a device that allowed researchers to study learning and problem-solving in animals under controlled conditions. In the 1950s, inspired by observations of infant monkeys in his laboratory, Harlow shifted his focus to the study of affection and attachment, work that would become his most famous and controversial legacy.
2. Pioneering Studies on Attachment and Love
2.1. The Wire Mother and Cloth Mother Experiments
Harlow’s most famous experiments involved isolating infant rhesus monkeys and providing them with surrogate mothers made of wire or cloth. When presented with a bare wire mother that provided food and a soft cloth mother that did not, the infant monkeys consistently preferred the cloth mother, clinging to it for comfort and security and only briefly visiting the wire mother to feed. These findings challenged the dominant behaviorist view that attachment was based primarily on the provision of basic needs like food.
2.2. The Nature of Love
Building on his work with the wire and cloth mothers, Harlow developed a new theory of the nature of love and affection. He proposed that love consists of three components: attachment, involving the seeking of closeness and contact; comfort, the feeling of security derived from contact; and security, the knowledge that the attachment figure will be available when needed. Harlow argued that these components of love are not innate but are developed through the infant’s early experiences with its caregivers, emphasizing the critical importance of contact comfort and responsive caregiving in fostering healthy emotional development.
2.3. The Effects of Maternal Deprivation
In another series of experiments, Harlow studied the effects of complete maternal deprivation on the development of infant monkeys. Monkeys raised in total isolation showed severe behavioral and emotional disturbances, including aggression, fear, and an inability to form normal social relationships. These findings highlighted the critical role of early social experiences in shaping later behavior and emotional functioning and had important implications for understanding the effects of institutionalization, neglect, and abuse on child development.
3. Controversies and Ethical Debates
3.1. Criticism of Harlow’s Methods
While groundbreaking, Harlow’s work has been the subject of significant ethical criticism. His experiments involved subjecting infant monkeys to severe emotional stress and deprivation, and some of his methods, such as the use of the “pit of despair” apparatus to induce depression, have been widely condemned as cruel. Critics argue that Harlow’s work reflects a lack of empathy for his animal subjects and a disregard for their suffering, questioning whether the scientific insights gained justify the emotional harm inflicted on the monkeys.
3.2. Animal Welfare Concerns
Harlow’s work has also been at the center of broader debates about the use of animals in psychological research. His experiments have been cited by animal rights activists as examples of the mistreatment of animals in the name of science. These concerns have led to increased regulation of animal research and a greater emphasis on minimizing animal suffering in experimental design. Today, the kinds of severe deprivation studies conducted by Harlow would be unlikely to receive approval from institutional animal care and use committees.
3.3. The Question of Applicability to Humans
While Harlow’s work has been highly influential in the field of child development, some have questioned the extent to which findings from studies on monkeys can be generalized to humans. Monkeys, while sharing many similarities with humans, also differ in important ways in terms of their social structures, developmental trajectories, and cognitive capacities. Nonetheless, Harlow’s work has been widely seen as providing important insights into the fundamental nature of attachment and the critical role of early experiences in shaping later development, informing practices in fields such as child welfare, early childhood education, and parenting.
4. Legacy and Impact
4.1. Contributions to Attachment Theory
Harlow’s work on attachment and love has been highly influential in the development of attachment theory, a major theoretical framework in child development and clinical psychology. His findings on the importance of contact comfort and responsive caregiving have been incorporated into the work of leading attachment theorists such as John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth. Attachment theory, which emphasizes the critical role of early emotional bonds in shaping later social and emotional functioning, has had a profound impact on our understanding of child development and has informed practices in fields such as parenting, education, and child welfare.
4.2. Implications for Child Welfare and Parenting
Harlow’s work on the effects of maternal deprivation has been influential in shaping policies and practices related to child welfare and institutional care. His findings have highlighted the importance of providing children with stable, responsive caregiving and have led to efforts to minimize the use of institutional care and to promote foster care and adoption for children who cannot remain with their biological parents. In the realm of parenting, Harlow’s work has reinforced the importance of responsive, sensitive caregiving and the provision of both physical and emotional nurturing, challenging earlier notions of children as passive recipients of care and emphasizing the active role of the child in shaping the attachment relationship.
4.3. Continuing Relevance in Developmental Psychology
Despite the passage of time and the evolution of research methods and ethical standards, Harlow’s work continues to be highly relevant in the field of developmental psychology. His findings on the nature of attachment, the importance of early experiences, and the effects of deprivation and abuse have laid the groundwork for much of the current research in this area. Contemporary researchers continue to build on Harlow’s legacy, exploring the complex interplay of biological, environmental, and social factors in shaping child development.
4.4. A Complex and Controversial Legacy
Harry Harlow’s legacy is a complex and controversial one. On one hand, his work has made profound contributions to our understanding of attachment, love, and the critical importance of early emotional experiences in shaping later development. His findings have informed practices in fields ranging from parenting to child welfare and have helped to shape the landscape of modern developmental psychology. On the other hand, Harlow’s methods have been rightly criticized as unethical and have raised important questions about the treatment of animals in psychological research. His work serves as a reminder of the need for constant reflection and evolution in research ethics and the importance of balancing scientific inquiry with the humane treatment of research subjects.
In conclusion, Harry Harlow’s pioneering work on attachment and love has left an indelible mark on the field of psychology. His experiments, while controversial, have provided profound insights into the nature of affection and the critical role of early experiences in shaping emotional and social development. As we continue to grapple with questions of how to nurture healthy development and foster resilience in the face of adversity, Harlow’s legacy serves as a reminder of the fundamental importance of love, nurturing, and responsive care in the lives of all primates, human and non-human alike. While we must continue to evolve our methods and ethical standards, the core insights of Harlow’s work endure, informing our understanding of what it means to be a social, emotional being in a complex world.
Bibliography
- Harlow, H. F. (1958). The nature of love. American Psychologist, 13(12), 673-685. – This influential paper discusses Harlow’s experiments with rhesus monkeys and the importance of contact comfort in the formation of attachment bonds.
- Harlow, H. F. (1959). Love in infant monkeys. Scientific American, 200(6), 68-74. – A popular article summarizing Harlow’s findings on the effects of maternal deprivation and the significance of social companionship in primate development.
- Harlow, H. F. (1962). The development of affectional patterns in infant monkeys. In J. DeMartino (Ed.), Sex and behavior: Status and prospectus (pp. 75-95). Holt, Rinehart, and Winston. – Explores Harlow’s research on attachment and social development in infant monkeys.
- Harlow, H. F., & Harlow, M. K. (1962). Social deprivation in monkeys. Scientific American, 207(5), 136-146. – Discusses the effects of isolation and social deprivation on psychological development in monkeys.
- Harlow, H. F. (1971). Learning to love. In L. R. Aronson, E. Tobach, D. S. Lehrman, & J. S. Rosenblatt (Eds.), Development and evolution of behavior: Essays in memory of T. C. Schneirla (pp. 75-95). W. H. Freeman. – A chapter discussing Harlow’s experiments and their implications for understanding emotional development.
- Harlow, H. F. (1974). Learning and satiation of response in intracranial self-stimulation. Journal of Comparative and Physiological Psychology, 87(2), 361-363. – Focuses on Harlow’s research on brain stimulation reward and its role in motivation and learning.
- Harlow, H. F., & Zimmermann, R. R. (1959). Affectional responses in the infant monkey. Science, 130(3373), 421-432. – A seminal paper detailing Harlow’s experiments on social isolation and the development of affectional bonds in monkeys.
- Harlow, H. F. (1995). The nature of love. In J. F. Rosenblatt, C. T. Snowdon, & M. L. Lehrman (Eds.), Advances in the Study of Behavior, Vol. 24 (pp. 87-173). Academic Press. – Revisits and reflects on Harlow’s earlier work on the nature of affection and attachment.
- Blum, D. E. (2002). Love at Goon Park: Harry Harlow and the science of affection. Basic Books. – A biography that explores Harlow’s life, his groundbreaking research with primates, and his impact on psychology.
- King, B. J. (2003). The scientific legacy of Harry Harlow. Oxford University Press. – A comprehensive examination of Harlow’s contributions to psychology, covering his experiments, theories, and influence on the field of developmental psychology.
Influential Psychologists























0 Comments