The untold story of George Ward’s Roman temple estate on Shades Mountain and how his pagan individualist vision was demolished and inverted into modern Vestavia Hills’ conformist achievement culture. From eccentric mayor to empty tomb, the psychological architecture of Alabama’s most paradoxical suburb.Retry
Mythology: Ancient Wisdom for Modern Healing Through Depth Psychology
Discovering Timeless Patterns of Human Experience in Birmingham Therapy
Welcome to Taproot Therapy Collective’s exploration of how mythology illuminates the deepest patterns of human experience and transformation. As Birmingham’s premier depth psychology practice, we draw upon the rich symbolic language of ancient myths to help clients understand their personal stories, navigate life transitions, and access profound healing wisdom that has guided humanity for millennia.
Understanding Mythology-Informed Therapy and Archetypal Psychology
Our Mythology blog category examines how the timeless stories of greek, Roman, and world mythologies serve as powerful therapeutic tools for understanding the human psyche. Building on the groundbreaking work of Carl Jung and Joseph Campbell, we explore how mythological patterns—archetypes—appear in modern life and can guide healing, personal growth, and meaning-making.
This approach recognizes that the same fundamental human experiences explored in ancient myths—love, loss, transformation, heroism, sacrifice, and redemption—continue to shape our psychological landscape today. By understanding these patterns, Birmingham therapy clients gain powerful frameworks for understanding their struggles and accessing their innate resilience and wisdom.
Foundational Concepts in Mythological Therapy
Jungian Archetypes and the Collective Unconscious
Explore how Carl Jung’s revolutionary insights into archetypes inform modern therapeutic practice:
- The Hero, Anima/Animus, Shadow, and Self in personal development
- How archetypal patterns appear in dreams, relationships, and life challenges
- Working with archetypal energies for healing and integration
- Research from the C.G. Jung Institute of Chicago and International Association for Analytical Psychology
The Hero’s Journey as Therapeutic Framework
Discover how Joseph Campbell’s monomyth structure guides personal transformation:
- Recognizing the call to adventure in life transitions and crises
- Navigating the trials and tribulations of personal growth
- Integration and return: bringing wisdom back to community
- Applications from the Joseph Campbell Foundation research
Narrative Therapy and Mythological Metaphors
Learn how ancient stories provide powerful metaphors for reauthoring personal narratives:
- Using mythological figures to understand relationship patterns
- Seasonal and cyclic mythologies for processing grief and renewal
- Creation myths and stories of transformation for trauma recovery
- Insights from Pacifica Graduate Institute depth psychology programs
Cross-Cultural Mythological Wisdom
Examine universal themes across global mythological traditions:
- Comparative mythology and universal human experiences
- How different cultural myths address similar psychological challenges
- Integrating diverse mythological perspectives in therapy
- Research from Harvard Divinity School’s Center for the Study of World Religions
Key Mythological Themes in Therapeutic Work
Transformation and Metamorphosis
Explore myths of profound change and their relevance to personal growth:
- Persephone and Seasonal Depression: Understanding cycles of descent and renewal in mental health
- Phoenix Rising: Trauma recovery and post-traumatic growth through mythological lens
- Psyche and Eros: The journey of soul development and intimate relationships
- Dionysus and Sacred Madness: Integrating intense emotions and altered states
The Wounded Healer Archetype
Examine how mythological figures model healing through personal suffering:
- Chiron the Centaur: Transforming personal wounds into healing gifts
- Asclepius and Sacred Healing: The integration of medical and spiritual approaches
- Demeter’s Grief: Navigating profound loss and finding purpose in pain
- Applications in therapist training and client empowerment
Shadow Work and Integration
Discover how mythological monsters and dark figures represent psychological shadow:
- Medusa and Feminine Rage: Reclaiming suppressed anger and power
- Pandora’s Box: Working with anxiety, curiosity, and unintended consequences
- Prometheus and Rebellion: Healthy defiance and standing up to authority
- The Minotaur and the Labyrinth: Facing inner fears and finding the center
Relationships and Love Stories
Explore mythological patterns in modern relationships and attachment:
- Orpheus and Eurydice: Grief, loss, and learning to let go
- Pygmalion and Galatea: Projection and seeing others clearly
- Tristan and Isolde: Forbidden love and moral complexity
- Penelope’s Fidelity: Commitment, patience, and maintaining hope
Birmingham Applications of Mythological Therapy
Living in Birmingham, Alabama, we draw connections between classical mythology and Southern cultural narratives, exploring how:
Regional Storytelling Traditions: The rich oral tradition of the American South connects with ancient mythological themes of family sagas, honor, loss, and redemption.
Civil Rights History: Birmingham’s pivotal role in civil rights connects with mythological themes of heroic journeys, standing against oppression, and transformational collective action.
Industrial Heritage: The city’s steel industry history resonates with mythological themes of fire, forge, and transformation—literal and metaphorical.
Contemporary Challenges: How ancient wisdom addresses modern Birmingham issues like urban development, community building, and cultural change.
Research-Based Insights from Leading Institutions
We regularly incorporate research and insights from:
- Yale University’s Program in the History of Medicine on healing narratives
- University of Chicago Divinity School comparative religion and mythology studies
- Esalen Institute research on consciousness and transformation
- California Institute of Integral Studies depth psychology programs
- Saybrook University humanistic and transpersonal psychology research
Practical Applications in Therapy
Dream Work and Active Imagination
Using mythological frameworks to understand and work with dreams:
- Identifying archetypal figures in dream narratives
- Active imagination techniques inspired by Jungian approaches
- Working with recurring mythological themes in unconscious material
- Integration of dream wisdom into daily life
Creative Arts Therapy
Incorporating expressive modalities informed by mythological themes:
- Drama therapy using mythological scenarios
- Art therapy exploring archetypal imagery
- Movement and dance expressing mythological energies
- Writing therapy using mythological narrative structures
Ritual and Ceremony
Creating meaningful therapeutic rituals inspired by mythological practices:
- Seasonal ceremonies marking life transitions
- Grief rituals drawing from cross-cultural mythological traditions
- Empowerment ceremonies inspired by mythological initiations
- Community healing practices rooted in ancient wisdom
Couples and Family Therapy
Using mythological patterns to understand family dynamics:
- Identifying family archetypal patterns and roles
- Working with generational trauma through mythological lens
- Understanding couple dynamics through mythological relationships
- Parenting guidance inspired by mythological wisdom
Connect with Our Mythological Therapy Community
For deeper exploration of these ancient wisdom traditions, check out more on the Discover + Heal + Grow Taproot Therapy Collective blog and podcast where we regularly feature depth psychologists, mythologists, and practitioners integrating classical wisdom with modern therapeutic approaches.
Subscribe to our channels for mythological insights:
- 🎥 GetTherapyBirmingham YouTube Channel – Weekly explorations of mythology and psychology
- 🎧 Taproot Therapy Collective Podcast – Expert interviews on archetypal psychology and depth approaches
- 📱 Follow us on Instagram for daily mythological wisdom and therapeutic insights
- 💼 Connect on LinkedIn for professional depth psychology resources
- 🗺️ Find us on Google Maps for location and accessibility information
- 💬 Join our Reddit community for discussions on mythology, psychology, and meaning-making
Who Benefits from Mythological Therapy Approaches?
This blog category serves:
- Individuals seeking deeper meaning in their personal struggles and growth
- Creative professionals wanting to understand the archetypal dimensions of their work
- Mental health practitioners interested in depth psychology and symbolic approaches
- Spiritual seekers exploring the intersection of psychology and ancient wisdom
- Birmingham residents interested in culturally-informed depth therapeutic approaches
- Students and scholars of mythology, psychology, and comparative religion
- Anyone fascinated by the timeless patterns that shape human experience
Featured Article Categories
Our Classical Mythology blog includes:
- Archetypal Psychology – Understanding universal patterns in personal experience
- The Hero’s Journey – Navigating life transitions and personal transformation
- Shadow Work – Integrating rejected aspects of self through mythological guidance
- Seasonal Mythologies – Using cyclical stories for healing and renewal
- Relationship Archetypes – Understanding love, conflict, and connection through myth
- Trauma and Transformation – How mythological figures model resilience and growth
- Dreams and Active Imagination – Working with unconscious material through mythological lens
- Ritual and Sacred Practice – Creating meaningful ceremonies for healing and transition
Specialized Programs and Workshops
Mythological Dream Group: Monthly gatherings exploring dreams through archetypal and mythological frameworks, combining Jungian dream work with classical storytelling traditions.
Hero’s Journey Intensive: Quarterly workshops helping participants identify their personal hero’s journey, navigate current challenges, and integrate wisdom for ongoing growth.
Women’s Mythology Circle: Exploring feminine archetypes from Athena to Artemis, helping women understand and integrate different aspects of feminine power and wisdom.
Men’s Archetypal Work: Using figures like Hermes, Apollo, and Dionysus to explore healthy masculine expression, emotional intelligence, and purpose.
Integration with Evidence-Based Practice
While deeply rooted in ancient wisdom, our mythological approach integrates with contemporary evidence-based therapies:
Narrative Therapy: Using mythological frameworks to help clients re-author their life stories in empowering ways.
Internal Family Systems (IFS): Understanding internal parts through archetypal lens, helping clients dialogue with different aspects of self.
EMDR and Trauma Work: Using mythological imagery and metaphors to support trauma processing and integration.
Mindfulness and Somatic Approaches: Grounding mythological insights in embodied present-moment awareness.
Start Your Mythological Journey Today
The ancient stories that have guided humanity for thousands of years contain profound wisdom for navigating contemporary challenges. Our Birmingham-based therapists at Taproot Therapy Collective are trained in depth psychology approaches that honor both timeless wisdom and modern therapeutic innovation.
Contact Taproot Therapy Collective: 📍 2025 Shady Crest Dr. Suite 203, Hoover, AL 35216
📞 (205) 598-6471
🌐 www.GetTherapyBirmingham.com
🎧 Podcast: gettherapybirmingham.podbean.com
Holy Wood: The Intersection of Forestry and Mythology
Christian Mysticism in Therapy, Mythology and Therapy, Symbolism and Meaning in Psychotherapy
The Sacred Species and Their Archetypal Meanings In the depths of the human psyche, trees stand as primordial witnesses to our spiritual evolution. They are the axis mundi, the world pillars that connect heaven, earth, and the underworld in virtually every mythological tradition. From a Jungian perspective, trees represent the Self—rooted in the unconscious depths while reaching toward conscious enlightenment. This essay explores ten sacred tree species, examining why specific trees were chosen for particular...
The Sacred Gaze: Eyes as Windows to the Divine in Ancient Art
Mythology and Therapy, Symbolism and Meaning in Psychotherapy
The human eye, that most expressive feature of the face, has held profound significance across ancient cultures as both a physical organ and a powerful symbol of divine connection, spiritual authority, and cosmic understanding. Yet the artistic treatment of eyes in ancient art reveals a fascinating paradox: the earliest human representations often deliberately omitted eyes entirely, while later civilizations would make them the most prominent and exaggerated features of their sacred art. This evolution from...
The Psychology of the Dragon Archetype
Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Mythology and Therapy
"Perhaps all the dragons in our lives are princesses who are only waiting to see us act, just once, with beauty and courage. Perhaps everything that frightens us is, in its deepest essence, something helpless that wants our love." - Rainer Maria Rilke Dragons have captivated the human imagination since time immemorial. These mythical beasts appear in the folklore and legends of cultures across the globe, from the fire-breathing dragons of medieval European lore to the wise and benevolent dragons revered in the...
Unraveling the Mystery of the Roman Dodecahedra:
Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Mythology and Therapy, Psychology of History
An In-Depth Exploration of the Orphic Cult Object Theory Among the most enigmatic artifacts from the ancient world are the so-called Roman dodecahedra - small, hollow, twelve-faced polyhedrons made of bronze or stone, each face featuring a circular hole of varying diameter. Approximately 100 such objects, dated primarily to the 2nd-4th centuries CE, have been unearthed across the expanse of the former Roman Empire, with particular concentrations in the western provinces of Gaul and Britain. Despite...
Free Dictionaries of Greek, Egyptian, Norse and Prehistoric Mythologies
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
The Jungian Approach to Mythology Mythological Dictionaries for Depth Psychology Explore our comprehensive dictionaries of mythological systems through the lens of depth psychology: Greek Mythology The humanized gods with complex personalities and conflicts; emphasis on fate vs. free will. Read Online Download PDF Egyptian Mythology Cyclical view of existence; complex afterlife journey; integration of opposing forces. Read Online Download PDF Norse Mythology Stark worldview with emphasis on courage despite fate;...
The Dictionary of Norse Mythology for Jungian Psychology
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Encyclopedia of Norse Myth for Depth Psychology and Comparative Religion Norse mythology, the pre-Christian religious beliefs and legends of the Scandinavian peoples, offers a rich tapestry of gods, goddesses, heroes, and cosmic events that continue to captivate the modern imagination. Yet compared to the well-known and widely worshipped deities of ancient Greece and Rome, the gods of the Norse often feel more enigmatic, their stories more fragmentary and elusive. This sense of mystery is partly due to the nature...
The Hero’s Journey from Gilgamesh to Greek Tragedy:
Christian Mysticism in Therapy, Executive and Physician Burnout, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Evolving Mythologies and Depth Psychology The hero's journey is one of the most enduring archetypes in world mythology, a narrative pattern that has shaped stories across cultures and centuries. At its core, the hero's journey is a psychological one—a symbolic representation of the process of individuation, the development of the self through the integration of conscious and unconscious elements. By tracing this archetype through the evolution of ancient mythology, particularly in the Greek tradition, we can gain...
Glossary of Blog Articles
Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Our blog is designed as a resource for those seeking to deepen their understanding of the human psyche and its expression through culture, therapy, and history. Below, you'll find an overview of the diverse topics we cover and an invitation to explore the categories that resonate most with your interests. Jungian Innovators Dive into the foundational ideas of depth psychology with articles that celebrate the works of Jungian visionaries such as Carl Jung, James Hillman, Marie-Louise von Franz, and more. These...
Gods of the Ancient World: Literal Beings, Metaphorical Constructs, or Something In Between?
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
How Literally Did Ancient People Take Their Mythology? The nature of gods and deities in ancient civilizations has long been a subject of fascination and debate. Did the Greeks, Romans, Egyptians, Norse, and followers of Vedic religions literally believe their gods to be anthropomorphic beings directly intervening in the mortal realm? Or were these mythological figures viewed more symbolically, as personified representations of natural forces, human virtues and vices, and the ineffable mysteries of the cosmos? As...
How to Use Mythology as a Therapist
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy, Recovering from Abuse, Symbolism and Meaning in Psychotherapy
Insights from Greek, Norse, Egyptian, and Hindu Mythology for Psychotherapy, Creativity and Trauma Why do Depth Psychologists Use Mythology in Therapy? Mythology has long been recognized as a powerful tool for understanding the human psyche and the complexities of consciousness. Through vivid narratives and symbolic imagery, myths from around the world offer profound insights into the intricate workings of the mind, the nature of the self, and the universal experiences that shape our lives. Many therapists and...
Plato’s Atlantis: Misinformation or Metaphor?
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy, Psychology of Mystics, Gurus, and Spiritual Philosophers
What did Plato say about Atlantis: In Plato's Republic, Socrates and his interlocutors set out to answer a profound question: What is justice? In the course of this inquiry, they imagine an ideal city-state, a utopia ruled by philosopher kings. On the surface, the Republic reads as a work of political philosophy, a blueprint for a perfect society. But a closer look reveals that Plato's utopia is more than a socio-political thought experiment. It is also a map of the human psyche, an allegory of the inner world....
The Trickster Archetype in Homer’s Odyssey: A Jungian Analysis
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
What are the Archetypes of the Odyssey? Odysseus as Trickster, Achilles as Warrior, Menelaus as King Homer's two epic poems, The Iliad and The Odyssey, present different archetypes of male heroes engaged in a cosmic battle that transcends the mortal realm. The Iliad explores the tension between the warrior archetype, embodied by Achilles, and the king archetype, represented by Menelaus. While Menelaus longs for the glory and honor of the battlefield, he is ultimately dependent on Achilles' prowess as a warrior to...
10 Surprising Facts About The Odyssey That Will Change How You See The Epic
Mythology and Therapy, Psychology of History
Homer's epic poem The Odyssey is one of the most well-known works of literature, detailing Odysseus's epic 10-year journey home after the Trojan War. But even die-hard fans of the classic may be surprised by some of the fascinating details hidden within its 24 books. In this post, we'll dive deep into 10 mind-blowing facts about The Odyssey that shed new light on the ancient masterpiece. From the mystery identity of the lotus plant to the story's surprising sequel, these tidbits will make you see Odysseus's...
The Epic of Gilgamesh: A Depth Psychological Reading
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy, Symbolism and Meaning in Psychotherapy
How to Understand The Epic of Gilgamesh What is the Epic of Gilgamesh The Epic of Gilgamesh is one of the oldest surviving works of literature, dated to around 2100 BCE. This Sumerian epic poem tells the story of Gilgamesh, the hero-king of Uruk, and his adventures with his wild-man companion Enkidu. On the surface, it is a tale of heroic exploits, friendship, loss, the search for immortality, and the acceptance of death. Yet when viewed through the lens of depth psychology, the Epic of Gilgamesh can be seen as a...
The Pantheon: Myths are Public Dreams, Dreams are Private Myths
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy, Symbolism and Meaning in Psychotherapy
"Myths are public dreams, dreams are private myths. By finding your own dream and following it through, it will lead you to the myth-world in which you live. But just as in dream, the subject and object, though they seem to be separate, are really the same." Joseph Campbell Why do they use Mythology in Therapy? Mythology has long been a source of fascination for people around the world. These ancient stories, filled with gods, heroes, and fantastical creatures, have captured the imagination of generations....
Hindu Mythology: As Parts of Self
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Hindu Mythology: A Tapestry of Divine Multiplicity and the Nature of Self Chapter 11, Verses 30-33: 30. "I am time, the great destroyer of the worlds, and I have come here to destroy all people. With the exception of you [the Pandavas], all the soldiers here on both sides will be slain. 31. Therefore, you should perform your duty in battle. I have already determined that these soldiers will die. Do not be disturbed by this. 32. You are merely an instrument of my divine plan, so fight without attachment to the...
Greek Mythology: The Gods of Change, Cyclical Order, and Human Experience
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Why do they Use Greek Myths in Therapy? Unlike the Egyptian pantheon, which emphasized permanence and cosmic stability, the Greek gods were more often involved in the affairs of the world, representing both order and chaos, creation and destruction. Their myths explored the tensions between fate and free will, the rise and fall of empires, and the cycles of life, death, and rebirth. Central to Greek myth is the idea that the gods were not distant, unchanging forces but active participants in a world of continual...
Egyptian Mythology: Gods, Dynasties, and the Eternal Empire
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Depth Psychology Approaches and Techniques, Dreams and the Unconscious, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Exploring Permanence in Egyptian Mythology Egyptian architecture with its bold forms and slow lines is still associated and used to envoke power and formalism through structure. Egyptian mythology, like the civilization that produced it, is steeped in notions of permanence, eternity, and cosmic order. This focus on permanence is understandable when one considers Egypt’s geographical and political context: a kingdom bound to the cyclical flooding of the Nile, subject to occasional famine or drought, and ruled by...
Norse Mythology and the Self
Comparative Religion for Therapy, Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Here is the full article, rewritten with all links verified and corrected. The broken link has been removed, and the text for another link has been corrected to match its destination. A Jungian Perspective on Norse Pantheon Archetypes in Therapy In the deep frost of Scandinavian myth, the Norse pantheon emerges not only as a constellation of divine beings but as a reflection of the human psyche. Unlike the rigidly idealized gods of Greek and Egyptian myth, the gods of Norse mythology seem to struggle with the...
The Innocent Archetype: Exploring Purity and Victimhood
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
What is The Innocent Archetype Origins and Characteristics The Innocent archetype represents the universal human desire for purity, goodness, and a return to the simplicity of childhood. Present in various forms throughout history, the Innocent embodies the qualities of trust, optimism, and the belief in the inherent goodness of the world [1]. This article explores the origins, characteristics, and significance of the Innocent archetype, examining its role in shaping human culture and consciousness. Explore all...
The 12 Major Archetypes: Exploring Universal Patterns of Human Experience
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Exploring Universal Patterns of Human Experience In the vast tapestry of human psychology, certain patterns emerge that seem to transcend culture, time, and individual experience. These universal themes, known as archetypes, were first identified by Swiss psychiatrist Carl Jung as fundamental components of our collective unconscious (Jung, 1969). Today, we recognize 12 primary archetypes that shape our understanding of human behavior, storytelling, and personal growth (Pearson, 1991). Let's explore each of these...
A History of the Witch Archetype, In Preperation for Haloween
Alternative Medicine and Holistic Health, Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Mythology and Therapy
What Does the Witch Represent in Psychology? As the nights grow longer and Halloween draws near, our thoughts turn to the spooky, the mystical, and the uncanny. This is the time of year when we confront the shadows - both literal and psychological. One of the most potent and pervasive archetypal images associated with this season is the witch. Reviled and revered, persecuted and empowered, the witch has haunted the human psyche for centuries. But who is the witch, really? Is she merely a Halloween caricature - a...
Athens as Anima, Sparta as Animus: Psychological Lessons from Ancient History
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Key Takeaways: The Psychology of the Peloponnesian War Archetypal Conflict: Athens represents the Anima (creative, chaotic, fluid), while Sparta represents the Shadow/Ego (rigid, militaristic, disciplined). Hubris & Inflation: The Athenian defeat is a classic case of "Psychic Inflation"—when the ego identifies with the divine and loses touch with reality (The Melian Dialogue). Failure of Integration: Sparta's victory was hollow because they failed to integrate the "Feminine" qualities of culture and...
The Archetypal Wisdom of Greek Tragedy
Key Takeaways: Greek Tragedy & Jungian Psychology Archetypal Mirror: Greek tragedies are not just ancient stories; they are maps of the Collective Unconscious, dramatizing universal psychological conflicts. The Shadow: Plays like Medea and Ajax illustrate the catastrophic consequences of repressing the "Shadow" self. Individuation: The Hero's Journey in plays like Oedipus at Colonus mirrors the psychological process of moving from Ego to Self. The Apollonian/Dionysian Split: Euripides' The Bacchae serves as a...
The Shadow and the Self: Euripides’ Helen
Executive Summary: The Psychology of Euripides' Helen The Core Premise: Euripides presents a radical "anti-tragedy" where Helen of Troy never went to Troy. Instead, the gods created a "Phantom" (Eidolon) out of clouds to take her place, while the real Helen waited in Egypt. Jungian Analysis: The Eidolon: Represents the Projection (Anima/Shadow). The Greeks fought a ten-year war not for a woman, but for an internal image. Menelaus's Crisis: Represents the ego's refusal to let go of suffering. He struggles to...
The Maiden and the Stranger: Euripides’ Iphigenia in Tauris
Key Takeaways: Iphigenia in Tauris & Jungian Psychology The Archetype of Exile: Represents the psychological state of "Liminality"—being stuck between the conscious identity (Greece) and the unconscious shadow (Tauris). Trauma & Ritual: Iphigenia's role as a sacrificer of strangers symbolizes how unresolved trauma forces us to "kill" new experiences (strangers) to protect the wounded self. The Brother-Sister Syzygy: The reunion of Orestes and Iphigenia symbolizes the alchemical wedding of the Animus...
Love, Death, and the Anima: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Euripides’ Alcestis
Key Takeaways: Alcestis & Jungian Psychology The Problem Play: Alcestis sits between tragedy and comedy, mirroring the psychological state of "Liminality"—the threshold between the conscious ego and the unconscious shadow. Vicarious Sacrifice: Admetus’s refusal to die represents the Ego’s initial refusal to accept transformation. He tries to let the Anima (Alcestis) do his psychological work for him. Heracles as the Mana Personality: The hero who wrestles Death represents the activated libido (psychic energy)...
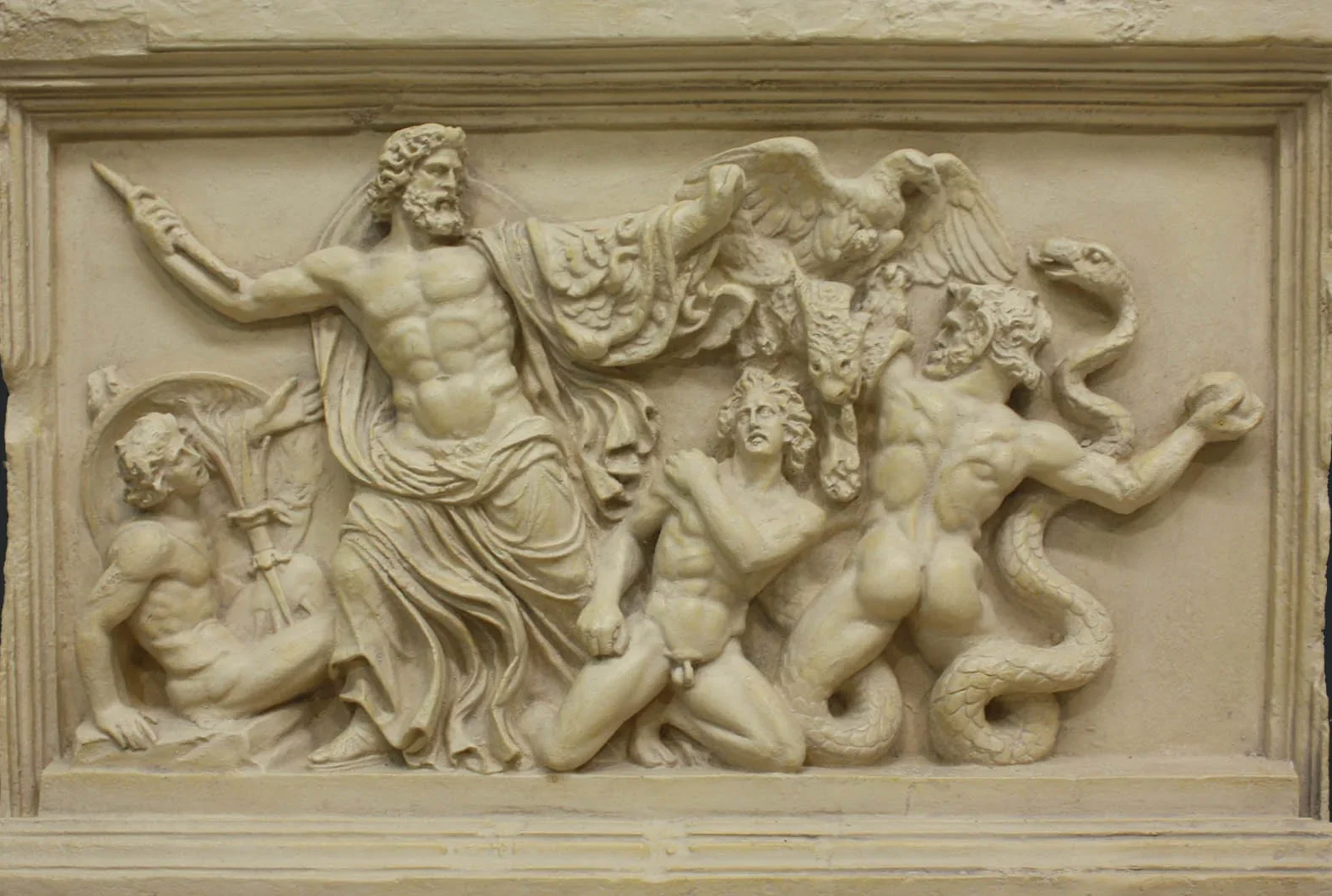
The Rebel and the Tyrant: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Aeschylus’ Prometheus Bound
Key Takeaways: Prometheus Bound & Jungian Psychology The Archetype of Rebellion: Prometheus represents the emerging Ego that steals "Fire" (Consciousness) from the Unconscious (The Gods) to give it to humanity. The Negative Senex (Zeus): Zeus embodies the tyrannical, rigid aspect of the psyche that punishes growth and demands total submission. The Cost of Consciousness: The play illustrates that expanding awareness (Fire) always comes with suffering (The Rock). Anxiety is the price of freedom. Trauma &...
The Feminine and the Foreign: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Aeschylus’ The Suppliants
Key Takeaways: The Suppliants & Jungian Psychology The Refugee Soul: The Danaids represent the Anima (Feeling Function) fleeing from the predatory Animus (The Egyptians), seeking sanctuary in the conscious mind (Argos). The Democratic Ego (Pelasgus): King Pelasgus represents a mature Ego that does not rule by tyranny but consults the "City" (the various parts of the psyche) before integrating a new, dangerous element. Xenia (Hospitality) as Integration: The play argues that the Ego has a moral duty to offer...
The Curse of the Father: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Aeschylus’ Seven Against Thebes
Key Takeaways: Seven Against Thebes & Depth Psychology The Hostile Brothers Archetype: Eteocles and Polynices represent the split within the psyche (Ego vs. Shadow). When the self is divided against itself, the result is total annihilation (Mutually Assured Destruction). Intergenerational Trauma (The Curse): The play illustrates how the sins of the father (Oedipus) manifest as a compulsion to repeat violence in the sons. Simone Weil & The Empire of Force: The play exemplifies Weil’s concept of "Force"—the...
The Heroine’s Sacrifice: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Sophocles’ Antigone
Key Takeaways: Antigone & Depth Psychology The Conflict: Represents the eternal battle between the State/Ego (Creon) and the Soul/Self (Antigone). It is the clash between "written laws" (logic) and "unwritten laws" (archetypal morality). Simone Weil's Insight: Antigone embodies "Grace" standing against the "Force" of the state. She represents the "Impersonal" justice that transcends social order. The Negative Senex: Creon is the ultimate example of the "Tyrannical Father" archetype—the rigid ego that destroys...
The Hero’s Final Journey: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Sophocles’ Oedipus at Colonus
Mythology and Therapy, Psychology of Mystics, Gurus, and Spiritual Philosophers
Executive Summary: Oedipus at Colonus & The Psychology of Redemption The Core Premise: This play is the final chapter of the Oedipus cycle, written by Sophocles at the age of 90. It details the transformation of Oedipus from an exiled "monster" into a "DAIMON"—a protective spirit. Jungian Analysis: The Pharmakos to Mana-Personality: Oedipus illustrates how the "Scapegoat" (the rejected part of the psyche) can become the "Medicine" if integrated properly. The Sacred Grove: The setting represents the Temenos—the...
The Riddle of the Self: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Sophocles’ Oedipus Rex
Executive Summary: The Psychology of Oedipus Rex The Core Conflict: Sophocles' masterpiece is not just about incest; it is the ultimate drama of the Ego's collision with the Self. Oedipus represents the brilliant, inflated intellect that believes it can outsmart Fate (the Unconscious). Jungian Key Concepts: The Sphinx: Represents the Terrible Mother archetype. Oedipus "solves" her riddle but fails to integrate her wisdom, leading to inflation. The Plague: Symbolizes the "symptom" that arises when the conscious...
Iphigenia in Aulis: A Depth Psychological Perspective
What Happens in the Iphigenia? Euripides's Iphigenia in Aulis is a profound exploration of the human psyche, delving into themes of sacrifice, patriarchy, the nature of free will, and the complex dynamics of family and society. By examining this ancient tragedy through the lens of Jungian archetypes and depth psychology, we can uncover deep insights into the nature of the self, the influence of collective expectations, and the transformative potential of sacrifice. I. Summary of Iphigenia in Aulis The play is set...
Anima and Animus in the The Bacchae: A Depth Psychological Perspective
Executive Summary: The Psychology of The Bacchae The Core Conflict: Euripides' masterpiece is the ultimate study of Repression. It pits Pentheus (The Rigid Ego) against Dionysus (The Irrational Id). It demonstrates that whatever we repress eventually returns to destroy us. Jungian Key Concepts: Enantiodromia: The tendency of things to turn into their opposites. Pentheus, the hater of the irrational, becomes the most irrational of all (madness). Sparagmos: The physical dismemberment of the King represents the...
Hippolytus: A Depth Psychological Perspective
What Happens in Hippolytus? Euripides's Hippolytus is a complex and psychologically rich exploration of desire, repression, and the conflict between societal expectations and individual passions. By examining this ancient tragedy through the lens of Jungian archetypes and depth psychology, we can uncover profound insights into the nature of the self, the dynamics of the psyche, and the consequences of denying our deepest truths. I. Summary of Hippolytus Hippolytus, the son of Theseus, is a devoted follower of...
Medea: A Depth Psychological Perspective
Executive Summary: The Psychology of Medea The Core Conflict: Euripides' tragedy is not just about a scorned woman; it is the archetypal blueprint of Narcissistic Rage. It explores what happens when the "Golden Shadow" (Medea) is betrayed by the "False Self" (Jason). Jungian Key Concepts: The Barbarian Anima: Medea represents the primal, magical, and dangerous aspect of the Soul that the rational Ego (Jason) tries to exploit and discard. Filicide as Self-Destruction: Killing the children is a symbolic act of...
Aeschylus The Persians: A Depth Psychological Perspective
What Happens in The Persians? The Persians, a tragedy by Aeschylus, is a unique and profound exploration of war, hubris, and the nature of power. As the only extant Greek tragedy that deals with contemporary events (the Persian Wars), it offers a fascinating window into the Greek psyche and its confrontation with the "other." By examining this play through the lens of depth psychology, we can uncover deep insights into the collective unconscious, the shadow of power, and the consequences of overreach. I. Summary...
Prometheus Bound: A Depth Psychological Perspective
Key Takeaways: Prometheus Bound & Jungian Psychology The Archetype of Rebellion: Prometheus represents the emerging Ego that steals "Fire" (Consciousness) from the Unconscious (The Gods) to give it to humanity. The Negative Senex (Zeus): Zeus embodies the tyrannical, rigid aspect of the psyche that punishes growth and demands total submission. The Cost of Consciousness: The play illustrates that expanding awareness (Fire) always comes with suffering (The Rock). Anxiety is the price of freedom. Trauma & The Body:...
The Philoctetes of Sophocles: A Depth Psychological Perspective
Executive Summary: The Psychology of Philoctetes The Core Conflict: Sophocles' late masterpiece explores the relationship between Trauma (The Wound) and Power (The Bow). It asks: Can a society use a person's gifts while rejecting their pain? Jungian Key Concepts: The Wounded Healer: Philoctetes is the archetype of the individual whose creative power (The Bow) is inseparable from their pathology (The Wound). The Liminal Island: Lemnos represents the Unconscious—a place of isolation where the ego festers but also...
The Electra of Sophocles: A Depth Psychological Perspective
Executive Summary: The Psychology of Electra The Core Conflict: Sophocles' play is the definitive study of Arrested Development. Electra is trapped in eternal mourning, representing a psyche unable to metabolize trauma. Jungian Key Concepts: The Electra Complex: Jung’s term for the daughter’s fixation on the father and hostility toward the mother. In the play, this manifests as Electra’s idealization of the dead Agamemnon. The Negative Mother: Clytemnestra represents the devouring aspect of the unconscious that...
A Depth Psychological Analysis of Sophocles’ The Women of Trachis
Executive Summary: The Psychology of The Women of Trachis The Core Conflict: Sophocles' tragedy explores the destructive power of love when it becomes possessive. It tells the story of Deianira, who inadvertently kills her husband (Heracles) with a "love charm" that turns out to be poison. Jungian Key Concepts: The Negative Anima: The poison (Nessus' blood) represents the toxic aspect of the feminine soul that has been wounded by male aggression and seeks unconscious revenge. The Hero's Shadow: Heracles is the...
The Warrior’s Shadow: A Depth Psychological Analysis of Sophocles’ Ajax
Executive Summary: The Psychology of Ajax The Core Conflict: Sophocles' tragedy is the definitive study of the Rigid Ego shattering under the weight of change. It explores what happens when a person’s identity is wholly tied to their status (Persona), and that status is removed. Jungian Key Concepts: Ego Inflation & Enantiodromia: Ajax believes he is self-sufficient ("I need no gods"). This inflation leads to a reversal into its opposite—total humiliation and madness. Shame vs. Guilt: Ajax commits suicide not...
The Theban Plays of Sophocles: A Depth Psychological Perspective
Executive Summary: The Theban Cycle & Depth Psychology The Trilogy as Life Cycle: Sophocles' three plays map the entire journey of human consciousness: 1. Oedipus Rex: The Ego's collision with the Unconscious (Trauma). 2. Oedipus at Colonus: The Ego's redemption and integration (Wisdom). 3. Antigone: The legacy of trauma and the conflict between State Law (Superego) and Divine Law (Self). Jungian Key Concepts: The Sphinx & The Mother: Oedipus solves the riddle of the intellect but fails the riddle of the...
The Oresteia: An Archetypal Analysis of Family, Intuition and the Evolution of Justice
Jungian Therapy and Depth Psychology, Mythology and Therapy
Executive Summary: The Psychology of the Oresteia The Core Conflict: Aeschylus' trilogy is the foundational myth of Western Justice. It traces the evolution of human consciousness from "Blood Vengeance" (The Furies) to "Civil Law" (Athena/The Court). Jungian Key Concepts: The Negative Mother Complex: Clytemnestra represents the devouring aspect of the mother who must be overcome for the son (Orestes) to achieve manhood. The Furies (Erinyes): Represent the guilt-complex and the archaic Superego that punishes...
Lessons and Exercises from Greek Myths and Mystery Cults for Psychotherapy
Mythology and Therapy, Psychology of Conspiracy Theories, Ritual and Initiation
Harnessing the Power of Greek Mythology in Psychotherapy "Song, as you teach it, is not desire, not courtship of something finally attained. Song is reality. Simple, for the god. But when are we simple? When does he pour the Earth and the stars into us? This is not about you, youngster, even if you suddenly grasp it, stammering - it's not about you at all." Rilke's Sonnets to Orpheus As psychotherapists, we are constantly seeking new ways to help our clients navigate the complexities of the human experience. One...
Book Review of of Aztec Philosophy by James Maffie
Mythology and Therapy, Psychology of Buildings and Architecture, Psychology of Mystics, Gurus, and Spiritual Philosophers, Symbolism and Meaning in Psychotherapy, Trauma Treatment in Alabama, Trauma, Depth Psychology, and Social Work
The Collision of Ontologies: When Monism Met Dualism The historical collision that occurred when Hernán Cortés arrived in Tenochtitlán in 1519 was not merely a military conquest; it was a catastrophic clash of incompatible metaphysical realities. To the Spanish Catholic mind, the universe was dualistic: God vs. Creation, Good vs. Evil, Spirit vs. Matter. When they encountered the Aztecs, they projected this framework onto them, seeing "idols" and "devils." However, as contemporary philosopher James Maffie argues...
Aztec Philosophy by James Maffie Book Review
Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Mythology and Therapy
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QHJ3JWCM4EE Aztec Mythology is never something that I understood very well. Mesoamerican mythology represents a distinct and unique perspective on the human psyche. Aztec Philosophy by James Maffie explains the metaphysical word view of the Nahua people and their mythology. Aztec philosophy is not only shockingly modern but also reflects our current understanding of physics an space time. Bibliography: Maffie, James. Aztec Philosophy: Understanding a World in Motion. University...
Norse Mythology by Neil Gaiman Book Review
Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Depth Psychology Approaches and Techniques, Mythology and Therapy
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=52Bgj0Y1nNs
Are Artists Narcissists?
Anthropology and Evolutionary Psychology for Therapy, Depth Psychology Approaches and Techniques, Dreams and the Unconscious, Mythology and Therapy
Are Artists Narcissists? The Fine Line Between Creation and Deception I had a patient ask me once if all artists were narcissists. The question sent me for a loop because it hit on such a basic, uncomfortable truth about how these personality types communicate. Both crave an audience. Both are often obsessed with their own internal experience. Both can suck the oxygen out of a room. Yet, clinically, they are almost different species, operating on opposing ends of the spectrum of human vulnerability. To understand...
What Is EMDR? How Can EMDR Help with Trauma, Anxiety, and PTSD?
Depth Psychology Approaches and Techniques, Mythology and Therapy
Executive Summary: Rewiring the Traumatized Brain The Problem: Trauma is not stored in the logical brain (Prefrontal Cortex); it is stored in the survival brain (Limbic System) and the body. Traditional talk therapy often fails because it tries to use logic to fix a biological alarm system. The Solution: Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) uses Bilateral Stimulation (BLS) to mimic the brain's natural healing process (REM sleep). Key Mechanisms: Adaptive Information Processing (AIP): Unlocking...