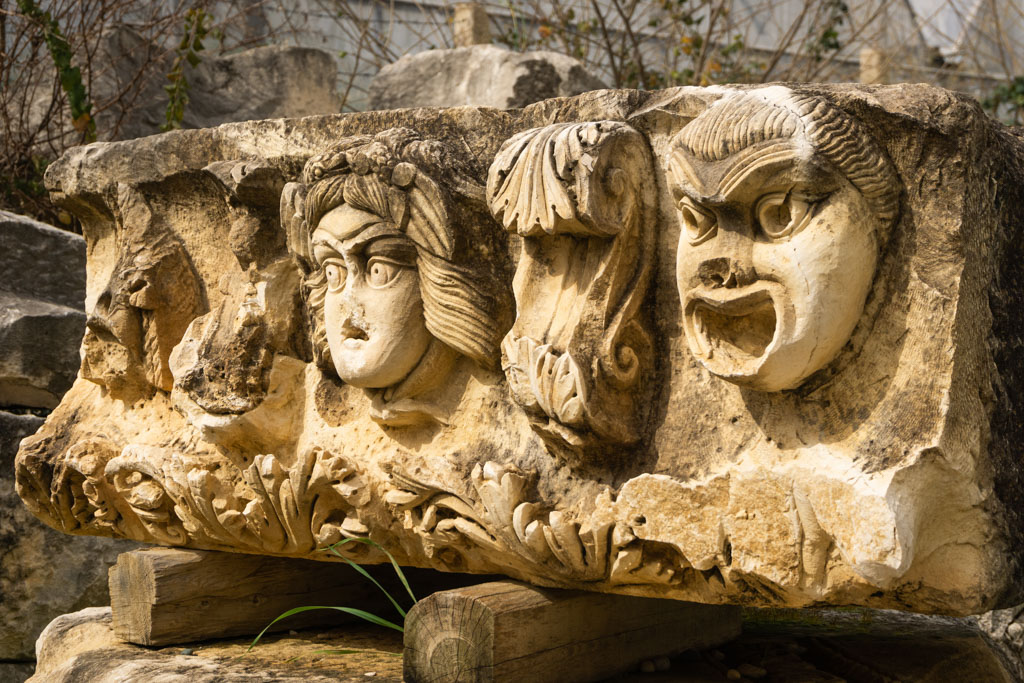

What Happens in Sophocles’ Ajax?
Sophocles’ Ajax is a powerful exploration of the archetypal Warrior and the consequences when this archetype is driven to extremes. Through the lens of Jungian depth psychology, we can understand Ajax’s tragic tale as a manifestation of the Warrior’s shadow – the destructive potential that lies beneath the surface of this otherwise noble archetype.
Summary of Ajax
Set during the Trojan War, Ajax tells the story of the Greek warrior Ajax, who is enraged when the armor of the fallen Achilles is awarded to Odysseus instead of himself. In his fury, he attempts to kill the Greek leaders Agamemnon and Menelaus, but Athena intervenes, clouding his mind so that he slaughters livestock instead. When he realizes what he has done, overcome by shame, Ajax takes his own life.
The second half of the play deals with the dispute over Ajax’s burial. The Greek leaders want to leave his body unburied as punishment for his attack, but Odysseus argues that Ajax should be honored as a great warrior despite his final actions. The play ends with Ajax’s burial.
Archetypal Figures in Ajax
Ajax: The Warrior’s Shadow
Ajax embodies the archetype of the Warrior – a figure of great physical prowess, courage, and honor. However, the play focuses on the shadow side of this archetype. Ajax’s sense of honor is so rigid and so central to his identity that when he feels it has been violated, it drives him to madness and suicide.
In Jungian terms, Ajax has become possessed by his shadow – the unconscious, often negative, aspects of his psyche. His pride, his inflexibility, and his rage – all qualities that may serve a warrior in battle – become destructive when he cannot integrate them with his conscious self.
Athena: The Trickster
Athena, in this play, takes on the role of the Trickster archetype. The Trickster is a figure who disrupts the normal order of things, often through deception or manipulation. Athena’s intervention in Ajax’s attack on the Greek leaders is a classic Trickster move – she prevents a terrible crime, but in a way that leads to Ajax’s humiliation and, ultimately, his death.
Athena represents the unpredictable, sometimes cruel, role that the gods (or the unconscious) can play in human life. Her actions highlight the precarious nature of human existence and the way in which our best-laid plans can be upended by forces beyond our control.
Odysseus: The Wise Ruler
Odysseus, in arguing for Ajax’s honorable burial, embodies the Wise Ruler archetype. This archetype represents leadership that is balanced, judicious, and compassionate. Despite being Ajax’s rival, Odysseus recognizes his value as a warrior and argues for a measured response to his actions.
In depth psychological terms, Odysseus represents the ego in its mature, individuated state. He is able to see beyond personal grievances and rigid codes of conduct, and to act with wisdom and humanity. His intervention suggests the possibility of integrating the Warrior’s shadow, of finding a way to honor the warrior’s spirit while also acknowledging his human fallibility.
Themes and Psychological Insights
The Perils of the Unintegrated Shadow
At its core, Ajax is a cautionary tale about the dangers of the unintegrated shadow. Ajax’s tragic end is not due to his warrior nature per se, but rather to his inability to recognize and integrate the shadow aspects of this archetype. His rigid adherence to a code of honor, his overwhelming pride, and his propensity for rage – all these qualities consume him because he cannot consciously acknowledge and work with them.
In Jungian psychology, integrating the shadow is seen as crucial to the process of individuation – of becoming a whole, balanced individual. Ajax’s story illustrates the perils of failing to do this work. When the shadow remains unconscious, it can possess us, leading to destructive, irrational behavior.
The Limits of the Warrior Archetype
The play also invites us to reflect on the limitations of the Warrior archetype itself. While the qualities of the Warrior – courage, strength, honor – are often lauded, Ajax shows us the dark side of this archetype when it is not balanced by other qualities.
Ajax’s single-minded focus on honor and glory leaves no room for flexibility, compassion, or self-reflection. In the end, it is these qualities, embodied by Odysseus, that are shown to be truly heroic. The play suggests that true strength lies not in rigid adherence to a code, but in the ability to adapt, to forgive, and to see the humanity in oneself and others.
The Role of the Gods (the Unconscious)
Athena’s role in the play can be seen as a metaphor for the workings of the unconscious. Like the unconscious, Athena’s intervention is sudden, unexpected, and has far-reaching consequences that Ajax cannot foresee or control.
This highlights the Jungian idea that the unconscious is not just a passive repository of repressed thoughts and feelings, but an active, autonomous force that can intervene in our lives in powerful ways. Ajax’s tragedy is a reminder of the need to develop a conscious relationship with this inner world, rather than being at the mercy of its unintegrated aspects.
The Possibility of Redemption
Despite its tragic arc, Ajax also hints at the possibility of redemption. Odysseus’ insistence on honoring Ajax in death suggests that it is never too late to recognize the humanity in another, to forgive and to learn from even the most terrible of actions.
In depth psychological terms, this points to the transformative potential of integrating the shadow. While Ajax himself is unable to do this in life, Odysseus’ gesture suggests that this integration is still possible on a collective level. By honoring Ajax’s warrior spirit while also acknowledging his human frailty, the community takes a step towards a more balanced, individuated understanding of the Warrior archetype.
Sophocles’ Ajax is a timeless exploration of the Warrior archetype and the dangers of the unintegrated shadow. Through the tragic story of Ajax, the play invites us to reflect on the limits of a rigid code of honor, the precarious nature of human existence, and the need to develop a conscious relationship with the unconscious.
At the same time, the play also hints at the possibility of redemption, of integrating the shadow and finding a more balanced way of being in the world. In this way, Ajax is not just a cautionary tale, but also a call to inner work – to the ongoing process of individuation that is at the heart of Jungian depth psychology.
Read About Other Classical Greek Plays and Their Influence on Depth Psychology
Classical Literature
Iphigenia in Aulis
























0 Comments