The Black Box of the Mind: From Dopamine to Sensory Gating
For decades, psychiatry operated under the “Dopamine Hypothesis”—the idea that mental illness, particularly schizophrenia, was simply a chemical imbalance of dopamine. We treated the brain like a car engine that just needed a quart of oil. However, modern neuroscience has revealed that this was a simplification. We now look toward the Sensory Gating Hypothesis, which suggests that the core issue isn’t just chemical levels, but the brain’s inability to filter (or “gate”) sensory input.
This shift from “chemical imbalance” to “information processing” mirrors the revolution happening in trauma therapy. Just as antipsychotics treat symptoms without always curing the underlying processing error, traditional talk therapy often manages symptoms without reaching the root. Therapies like EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing), Brainspotting, and ETT (Emotional Transformation Therapy) are not “talking cures”; they are surgical interventions for the subcortical brain. They bypass the thinking mind to access the “Body Brain”—the deep, non-verbal structures where trauma actually lives.
The Evolution of Brain-Based Medicine
The history of psychotherapy is a movement from the “top-down” (analyzing thoughts to change feelings) to the “bottom-up” (changing the body to shift thoughts). While Freud gave us the language of the unconscious, it was the discovery of the brain’s processing systems that gave us the tools to rewire it.
Timeline of Neuro-Experiential Therapies
| Year | Event / Publication |
| 1987 | Francine Shapiro discovers that eye movements can reduce the intensity of disturbing thoughts, leading to the development of EMDR. |
| 2003 | David Grand, an EMDR trainer, discovers “Brainspotting” while treating a figure skater. He realizes that where we look affects how we feel. |
| 2009 | Steven Vazquez publishes Emotional Transformation Therapy, mapping how specific wavelengths of light and color can access different emotional centers in the brain. |
| 2013 | David Grand publishes Brainspotting: The Revolutionary New Therapy for Rapid and Effective Change, formalizing the Dual Attunement Frame. |
| Present | Research into the Default Mode Network (DMN) and the Midbrain validates these therapies as mechanisms for memory reconsolidation. |
Major Concepts: The Subcortical Revolution
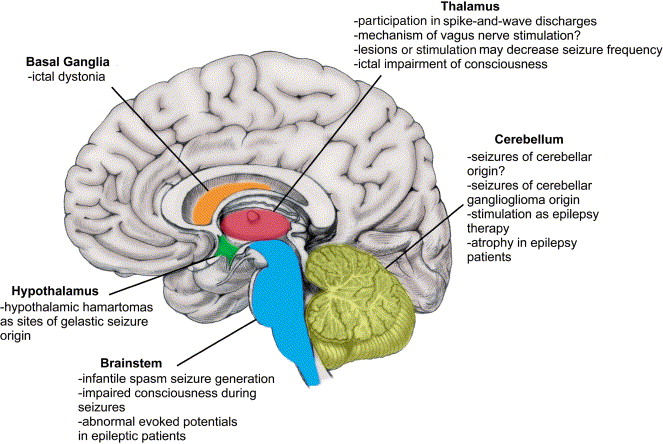
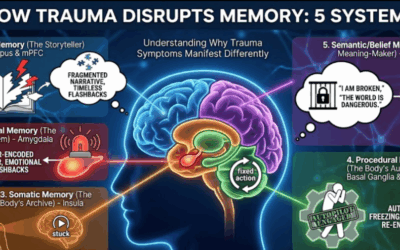
The Body Brain: Basal Ganglia and Implicit Memory
We often think of memory as a movie we can replay (Explicit Memory). However, trauma is stored as Implicit Memory—procedure, sensation, and reflex. This type of memory is housed in the Body Brain, specifically the Basal Ganglia and the Cerebellum.
The Basal Ganglia “learns” emotional responses the same way it learns to ride a bike. Once a traumatic reaction (like freezing in danger) is learned here, no amount of talking in the Prefrontal Cortex can “unlearn” it. Brainspotting targets these subcortical structures directly, using eye position to access the “files” that talk therapy cannot reach.
The mechanism of “Reset”
Brain-based therapies work by spiking the neural activation associated with a trauma while keeping the body safe. This paradox—high activation + physical safety—forces the brain to “reset” the association. This is known as Memory Reconsolidation. The brain realizes, “I am feeling the terror, but I am safe.” This breaks the link between the trigger (e.g., a loud noise) and the survival response (e.g., panic).
The Conceptualization of Trauma: The Frozen Midbrain
David Grand and other innovators view trauma not as a “psychological” problem but as a physiological one. When an event overwhelms the nervous system, the processing of that event is interrupted. The memory is not filed away in the past; it gets stuck in the midbrain (specifically the Superior Colliculus and Periaqueductal Gray).
Differentiation from Traditional Models
While talk therapy operates in the Neocortex (logic, language, time), trauma operates in the Limbic System and Brainstem (survival, instinct, timelessness). This is why a client can say, “I know I’m safe,” while their heart is racing. Brainspotting uses the visual field to locate the specific “capsule” of trauma in the midbrain. By holding the gaze on that spot (the “Brainspot”), the therapist acts as a “biological auxiliary cortex,” holding the space for the client’s brain to finish the processing it couldn’t do at the time of the event.
Clinical Application: The Delayed Processing Effect
Patients often report that the real work of Brainspotting happens after the session. Because the intervention targets deep subcortical structures, the “upstairs brain” (Prefrontal Cortex) takes time to catch up. This is why clients may experience vivid dreams or emotional releases 2-3 days post-session. This is the brain physically reorganizing its memory files during Slow Wave Sleep and REM cycles, moving data from the “active threat” folder to the “long-term memory” folder.
Lasting Influence & Legacy
The shift toward brain-based medicine has fundamentally altered the landscape of mental health. We are moving away from the “black box” of the mind and into the precise cartography of the brain. Techniques like Brainspotting and Emotional Transformation Therapy are paving the way for a future where therapy is faster, deeper, and less reliant on the client’s ability to articulate the unspeakable. They validate the reality that the body keeps the score, and they provide the tools to settle the debt.
Bibliography
- Corrigan, F. M., & Grand, D. (2013). “Brainspotting: Recruiting the midbrain for accessing and healing sensorimotor memories of traumatic activation.” Medical Hypotheses, 80(6), 759-766.
- Grand, D. (2013). Brainspotting: The Revolutionary New Therapy for Rapid and Effective Change. Sounds True.
- Shapiro, F. (2017). Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) Therapy, Third Edition. The Guilford Press.
- Schore, A. N. (2019). Right Brain Psychotherapy. W. W. Norton & Company.
- Panksepp, J., & Biven, L. (2012). The Archaeology of Mind: Neuroevolutionary Origins of Human Emotions. W. W. Norton & Company.
















0 Comments